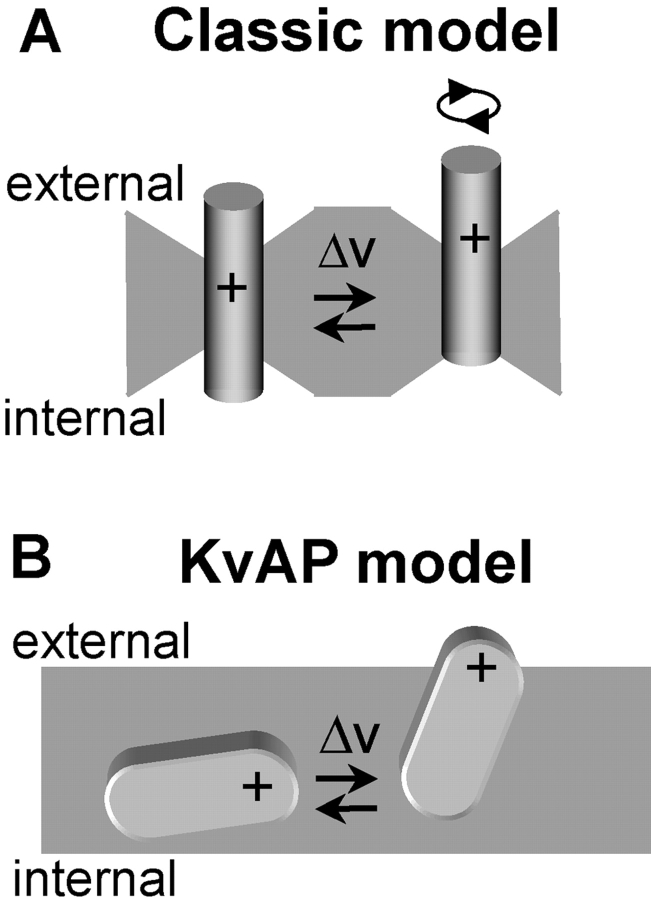
Figure 1.
Models of voltage sensor movement during changes in membrane voltage. (A) A model for depolarization-activated channels (classic model). For clarity, a single S4 α-helix is shown which sits in a water-filled crevice with a narrow constriction, separating the internal from external environment. In response to membrane depolarization, S4 moves outward, causing translocation of a series of positively charged residues either by translation or rotation. (B) In the KvAP model, a voltage sensor paddle (formed of S3b-S4 helixes; one of four in the channel complex) moves through the lipid bilayer.