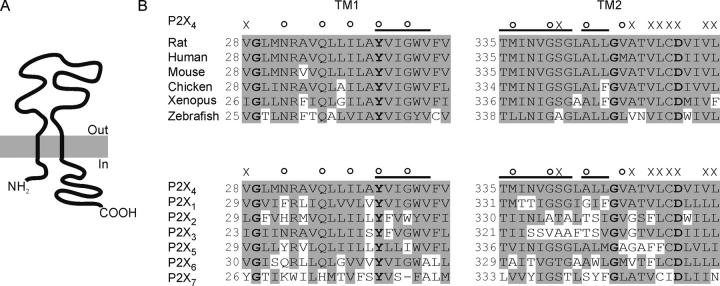
Figure 1.
Putative transmembrane regions of P2X receptor channels. (A) Schematic representation of the general topology of a P2X receptor channel subunit. (B) Sequence alignment of TM1 (left) and TM2 (right) of P2X4 receptor channels from different species (top) and of rat P2X1–P2X7 (bottom). Bold residues are identical across all known P2X receptor channels (except for a Y to F substitution in Xenopus P2X7). The major findings of this study are summarized above the sequences. X indicates mutations to tryptophan that result in nonconducting channels. Empty circles and bars indicate positions and regions of large perturbations in EC50 induced by the mutations, respectively.