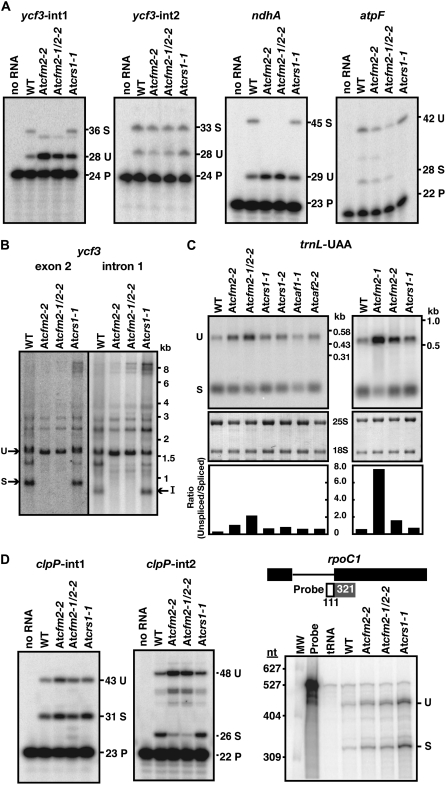
Figure 7.
Chloroplast RNA Splicing Defects in At CFM2 Mutants.
(A) Poisoned-primer extension assays monitoring splicing of chloroplast group II introns. Total leaf RNA (10 μg) from wild-type, At cfm2-2, At cfm2-1/At cfm2-2, and At crs1-1 seedlings was analyzed. The length in nucleotides of each predicted product is indicated. The size of the unlabeled product in the ycf3-int1 assay matches that predicted for the product from an unspliced RNA template in which the last nucleotide of the intron (a cytidine residue) is edited. U, unspliced; S, spliced; P, primer.
(B) RNA gel blots confirming a ycf3-int1 splicing defect in At CFM2 mutants. Total leaf RNA (5 μg) was probed with exon 2 or intron 1 specific probes, as indicated. I, excised intron; S, spliced mRNA; U, unspliced precursor that includes intron 1.
(C) RNA gel blots demonstrating trnL-UAA splicing defect in At CFM2 mutants.
Leaf RNA (1 μg) from seedlings with the indicated genotypes was analyzed by RNA gel blot hybridization using a probe that includes both exon and intron sequences. The same blots stained with methylene blue are shown below; 25S and 18S are cytosolic rRNAs. The ratio of unspliced-to-spliced RNA was quantified with a phosphor imager and is shown in the bar graphs. U, unspliced; S, spliced.
(D) Analysis of the splicing of chloroplast introns found in Arabidopsis but not in maize. Poisoned-primer extension assays were used to monitor clpP-int1 and clpP-int2 splicing, as described in (A). The unlabeled band in the clpP-int2 assays may represent a structure-induced reverse transcriptase stop within the intron, as its abundance is proportional to that of the full-length product from an unspliced template. A ribonuclease protection assay using the diagrammed probe was used to monitor rpoC1 splicing. U, unspliced; S, spliced; P, primer.