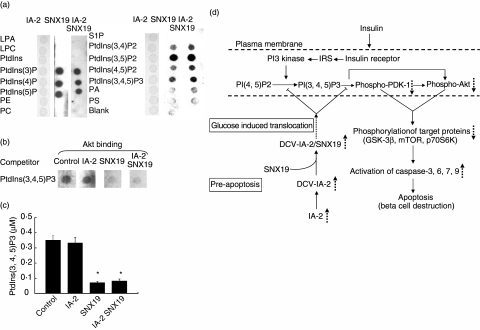
Fig. 6.
Binding of sorting nexin (SNX)19 to PtdIns. (a) Purified IA-2, SNX19 or a combination of the two was overlaid on a membrane spotted with different PtdIns and binding was determined. (b) Competitive Akt/protein kinase B (PKB) binding to PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 in the presence or absence of IA-2 and/or SNX19. (c) SNX19, but not IA-2, inhibits the conversion of PtdIns(4, 5)P2 to PtdIns(3, 4, 5)P3 by PI3 kinase as determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Mean ± s.e. of three separate experiments. *P < 0·05. (d) Schematic diagram depicting the proposed mechanism by which overexpression of IA-2 leads to apoptosis. Overexpression of IA-2 increases the number of DCV in mouse insulinoma MIN-6 cells [11]. SNX19 binds to the cytoplasmic domain of IA-2 and in the presence of high glucose dense core vesicles (DCV) are translocated to the plasma membrane. As there are more DCV in IA-2 transfected cells this would result in the delivery of more SNX19 to the plasma membrane, where SNX19 could block the conversion of PI(4,5)P2 to PI (3,4,5)P3 and inhibit the phosphorylation of phosphoinositide-dependent kinase (PDK)-1 and Akt/protein kinase B (PKB). This in turn would down regulate the phosphorylations of proteins in the PDK-1 and Akt/PKB signalling pathway resulting in the activation of caspases and beta cell apoptosis. LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPC, lysophosphocholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; PA, phosphatidic acid; PS, phosphatidylserine.  , increase,
, increase,  , decrease,
, decrease,  , inhibition,
, inhibition,  , translocation.
, translocation.