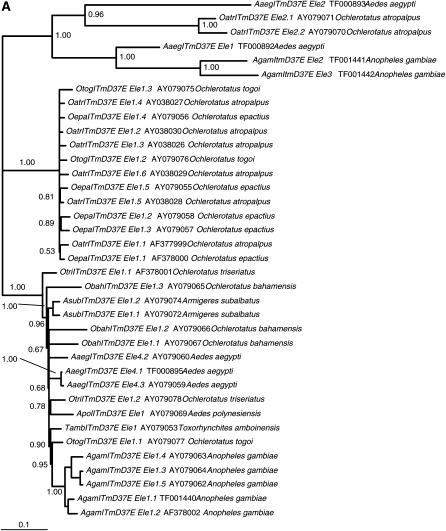
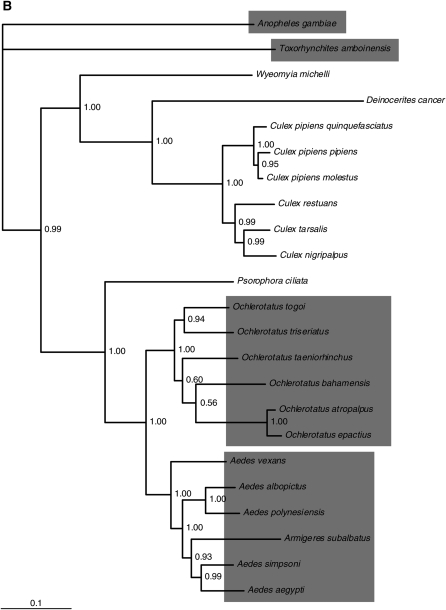
Figure 2.—
Comparison of host and ITmD37E phylogenies. Both trees shown are consensus trees (>50%) constructed using MrBayes version 3.1.2 (Huelsenbeck and Ronquist 2001; Ronquist and Huelsenbeck 2003). Clade credibility values are shown at each node. The scale represents substitutions per site. (A) ITmD37E phylogeny based on nt sequence from ORFs. Tree is rooted with divergent mosquito ITmD37E elements seen at the top of the tree. Element name, accession number, and species name are given when applicable. Information regarding sequences used in this study can be found in supplemental File S2 (http://www.genetics.org/supplemental/). (B) Mosquito host phylogeny based on Vg-C nt sequence. Tree is rooted with An. gambiae Vg-C. The five genera that have species containing ITmD37E sequences are shaded. The Armigeres subalbatus sequence is found within the Aedes group, which is consistent with previous analyses (Isoe 2000). Most Vg-C sequences were obtained from Isoe (2000). See supplemental File S1 for methods and supplemental File S3 for alignments.