Fig. 1.
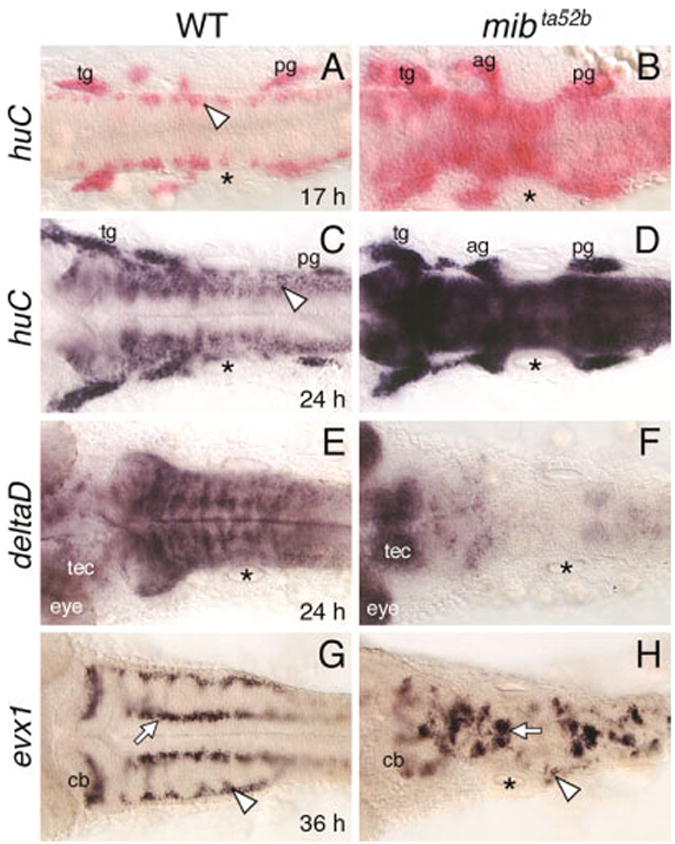
Defective neurogenesis in the mind bomb mutant hindbrain. All panels show dorsal views of the hindbrain with anterior to the left. The asterisks in all panels indicate the location of the otocyst. A,B: In a 17 hours postfertilization (hpf) wild-type embryo (WT; A), huC is expressed in small clusters of cells (arrowhead) located at the lateral margins of the hindbrain. In a mib mutant (B), huC-expressing cells are found throughout the hindbrain, with higher densities at some axial levels. C,D: In a 24 hpf wild-type embryo (C), the huC expression domain has expanded medially, and expressing cells are found at all axial levels, including the caudal hindbrain (arrowhead). In a mib mutant (D), the hindbrain at all axial levels is filled with huC-expressing cells. E,F: In a 24 hpf wild-type embryo (E), deltaD is expressed extensively, with higher expression in segmentally reiterated cell clusters. In the mib mutant (F), deltaD expression is greatly reduced or absent in the hindbrain and sharply higher in the tectum (tec) and eye. G,H: In a 36 hpf wild-type embryo (G), evx1 is expressed in commissural neurons (arrowhead), cerebellar neurons (cb), and putative interneurons (arrow). In a mib mutant (H), the evx1-expressing commissural neurons are greatly reduced (arrowhead), while the cerebellar neurons and interneurons (arrow) are disorganized and fused, and reduced in number. ag, acoustic ganglion; cb, cerebellum; tec, tectum; tg, trigeminal ganglion; pg, posterior lateral line ganglion.
