Fig. 3.
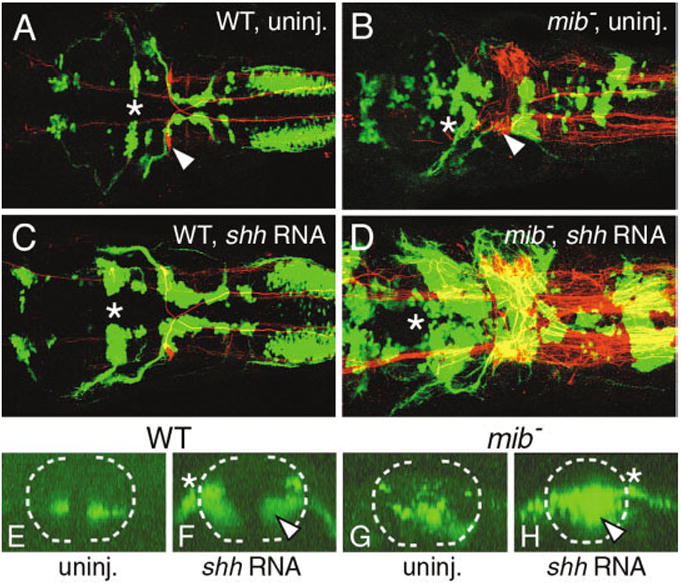
Shh overexpression induces branchiomotor neurons (BMNs) in the mind bomb mutant hindbrain. A–D show dorsal views of the hindbrain with anterior to the left and are composite confocal images, identifying GFP-expressing motor neurons in the fluorescein channel and 3A10-labeled Mauthner reticulospinal neurons and axons in the rhodamine channel. Asterisks in A–D indicate the location of the trigeminal (nV) motor neurons in rhombomere 2 (r2). E–H show confocal projections (virtual cross-sections) of GFP-expressing cells at the level of r4 and r5, and illustrate the effects of shh overexpression on nVII motor neurons. The broken line marks the outline of the neural tube, with dorsal to the top. The asterisks in F and H indicate the exit point of nVII axons from the neural tube. A: In a control wild-type embryo (WT), one Mauthner (M) neuron (arrowhead) is found on each side in r4 and BMNs are found in characteristic locations and numbers. E: In addition, the nVII motor neuron cell bodies are found in the ventral neural tube. C: In a shh RNA-injected wild-type embryo, the various GFP-expressing BMN clusters contain significantly larger numbers of cells, while M cell number is not affected. F: While most of the ectopic nVII motor neurons are found in the dorsal neural tube, a significant number (arrowhead) is also found in ventral locations. B: In a control mib mutant, there are excess M cells (arrowhead) and the BMNs exhibit the mib mutant phenotype. G: The nVII neurons are distributed randomly in the ventral half of the neural tube. D: Upon shh RNA injection, there is a sharp increase in the various BMN populations, while M cell number is not affected. H: Significantly, many of the ectopic nVII motor neurons (arrowhead) in the mutant are found in the ventral neural tube. The mutant embryo shown in D had an unusually large increase in motor neuron number at all axial levels.
