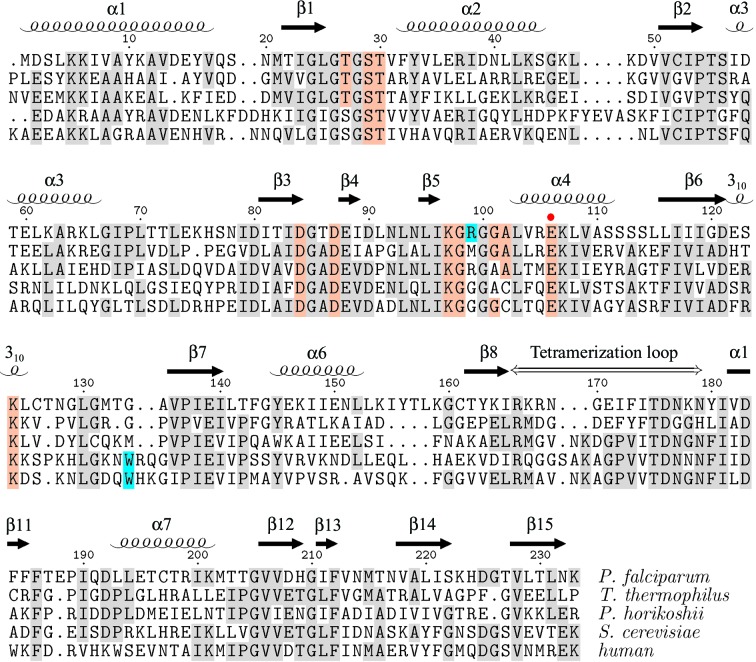
Figure 2.
Structure-based sequence alignment of ribose 5-phosphate isomerase RpiA from P. falciparum (2f8m), T. thermophilus (1uj5), Py. horikoshii (1lk5) and S. cerevisiae (1xtz). Residue numbering and secondary-structure elements are those of the present structure. The alignment was produced by the CEMC server (Guda et al., 2001 ▶, 2004 ▶). The human RpiA sequence, for which no structure has yet been reported, was added separately. Conserved residues that directly contact the ribose 5-phosphate in the 1uj5 structure are indicated by colored shading and the proposed general base/acid (Glu106 in P. falciparum) is indicated by a red dot (Ishikawa et al., 2002 ▶; Zhang et al., 2003 ▶; Hamada et al., 2003 ▶). Residues contributing to a significantly different binding site surface in the P. falciparum and human enzymes are highlighted in cyan. The figure was generated using TEXshade (Beitz, 2000 ▶).