Figure 3.
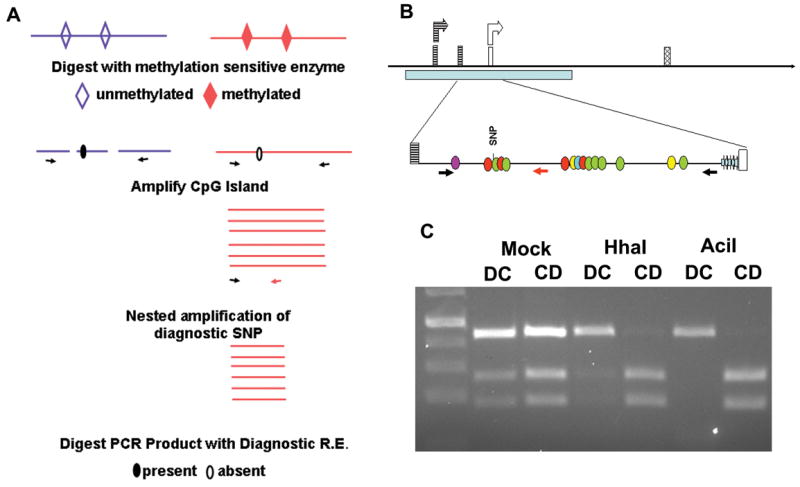
The promoter region of Sfmbt2 displays maternal methylation.
(a) Methylation sensitive PCR strategy. Illustrated is the outcome in a DC cross, where the maternal Domesticus allele, which lacks the MseI site, survives digestion with a variety of methylation sensitive enzymes. MseI is a frequent cutter (TTAA), thus necessitating nested PCR following digestion of genomic DNA and amplification of the CpG island.
(b) Schematic diagram of Sfmbt2 promoter region. Two start sites corresponding to Promoter 1 (striped boxes) and Promoter 2 (open boxes) generate two different leader 5′ UTRs that are spliced onto the first common exon (hatched). A CpG cluster spans both start sites (pale blue bar), including a 57 bp block of imperfect GC-rich repeats (thick, pale blue arrows, not to scale, bottom line) immediately 5′ of Promoter 2. Methylation-sensitive CpGs are indicated by coloured circles (BsmBI, purple; HhaI, red; AciI, green; HpaII, yellow; SmaI, turquoise). (c) Genomic DNA from e14.5 DC or CD F1 placentas was digested overnight with methylation sensitive restriction enzymes, or with buffer alone (mock). Digested DNA was amplified with PrDMRCastF1 and PrDMRR11 primers (Table 2). The resulting PCR product was subjected to 10 cycles of nested PCR with PrDMRCastF1 and PrDMRCastR1. This generates a 447 bp fragment that contains a polymorphic SNP. Digestion of the Castaneus allele with MseI generates 265 bp and 182 bp fragments, while the Domesticus allele remains undigested. Illustrated here are the results for genomic DNA digested with HhaI or AciI. Similar results were obtained following digestion with SmaI, BsmBI, HpaII, and various combinations.
