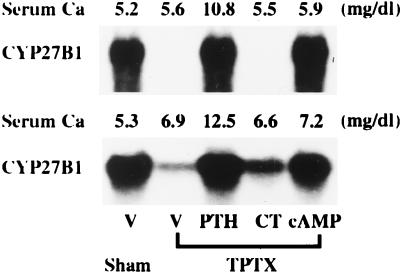
Figure 2.
Comparative effects of CT, PTH, and cAMP on the expression of renal CYP27B1 mRNA in vitamin D-deficient TPTX rats infused with 5 mM or 10 mM CaCl2. Male weanling rats were maintained for 3 weeks on a synthetic vitamin D-deficient, low-Ca diet (0.03% Ca, 0.6% P). At the end of the feeding period, rats were TPTX under light ether anesthesia and were infused with either 5 mM (Upper) or 10 mM (Lower) CaCl2 at a rate of 3 ml/h for 48 h. Infusion of either 5 mM or 10 mM CaCl2 for 48 h increased the serum levels of Ca to 5.6 and 6.9 mg/dl, respectively. CT, PTH, cAMP, or vehicle (V: sodium acetate) was administered for the last 12 h of the infusion period at a dose of 0.5 unit/h, 3 μg/h, 250 nmol/h, or 0.5 nmol/h, respectively. Renal poly(A)+ RNA was purified from total RNA by using Oligotex dT 30, and Northern blots were probed with cDNAs for CYP27B1. Similar results were obtained in three independent sets of experiments.