Fig. 5. Expression of dnCDK9 in PBLs inhibits HIV-1 replication in single round assays, but does not affect T cell activation as determined by the expression of T cell activation and cell cycle markers.
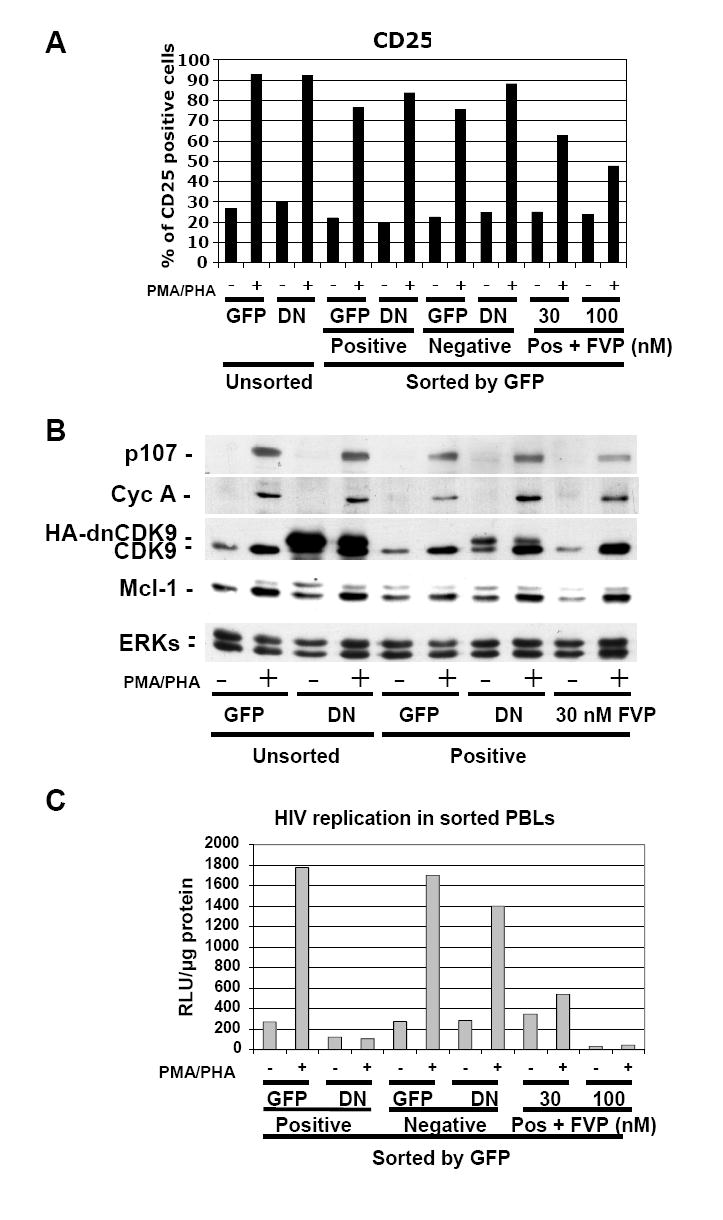
PBLs were transduced with HA-dnCDK9/EGFP (DN) or EGFP (GFP) lentiviruses and sorted 48 hrs later to separate a population of cells enriched with EGFP expressing cells (Positive) from a population with no detectable EGFP expression (Negative). Sorted EGFP-transduced control PBLs were also treated with FVP as indicated (Pos + FVP). Sorted and unsorted PBLs were then stimulated with PMA/PHA and processed for analysis of CD25 surface marker expression (A) or WB (B) analysis as in Fig. 4. In contrast to FVP, HA-dnCDK9 does not affect CD25 expression at the T cell surface (A) or cell cycle markers (B). (C) The cellular fractions described above were infected with HXB2 pseudotyped HIV-luc viruses and HIV-1 transcription/replication was determined at 48 hrs post-stimulation by measuring luciferase activity. HA-dnCDK9 inhibits HIV-1 replication more potently that 30 nM FVP without the cellular effects associated with FVP.
