Figure 1.
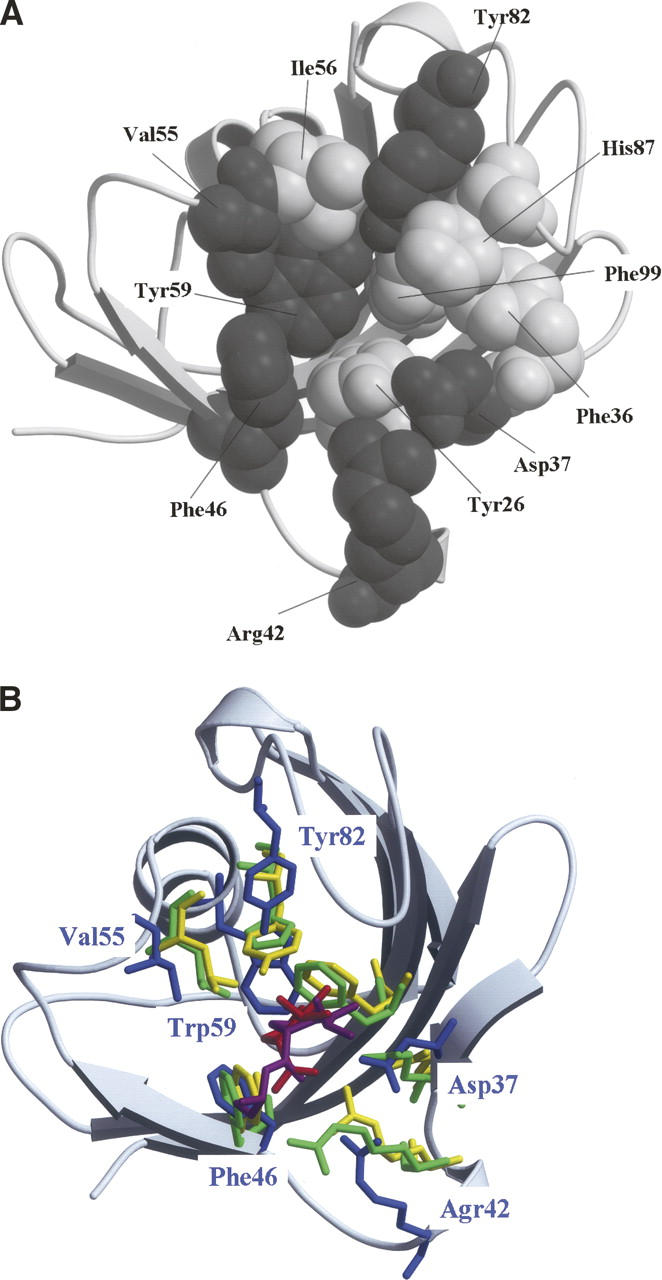
Structures of FKBP12. (A) Eleven amino acid residues constituting the substrate-binding cavity of FKBP12 are drawn using the space-fill model. Gray and white spheres represent the residues investigated in this study (Asp37, Arg42, Phe46, Val55, Trp59, and Tyr82) and the remaining five residues (Tyr26, Phe36, Ile56, His87, and Phe99), respectively. (B) When the substrate-binding cavities of FKBP12 (Wilson et al. 1995), human cyclophilin A (hCyPA) (Ke et al. 1993), and E. coli cyclophilin A (eCyPA) (Konno et al. 1996) were superimposed on each other, the corresponding six amino acid residues were drawn using the stick model: Asp37, Agr42, Phe46, Val55, Trp59, and Tyr82 of FKBP12 (blue); Arg55, Phe60, Gln63, Phe113, Leu122, and His126 of hCyPA (green); Arg43, Phe48, Gln51, Phe99, Leu108, and Tyr120 of eCyPA (yellow). The root-mean-square deviations among the main chain atoms were calculated within 4.0 Å. The residues of FKBP12 are labeled blue. The substrates of hCyPA and eCyPA are also drawn using the stick model: Red and magenta sticks denote the dipeptide Ala-Pro bound to hCyPA and the tripeptide Ala-Pro-Ala bound to eCyPA, respectively. The secondary structure representation of FKBP12 was produced using MolScript and rendered using Raster3D (gray) in both panels.
