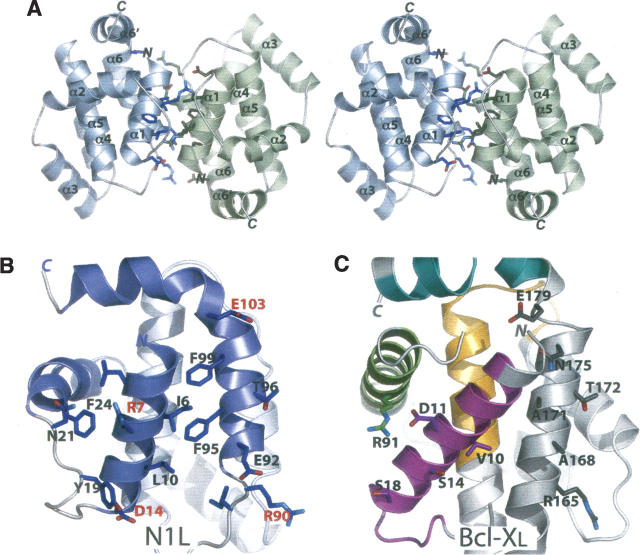
Figure 2.
N1L adopts a dimeric structure. (A) Stereo view of the N1L homodimer. The α1 and α6 helices from one N1L monomer (blue) interact in an antiparallel way with equivalent helices in another monomer (green). N and C termini, and helices of each subunit are labeled. (B) Specific α1 and α6 residues at the N1L dimer interface. In the antiparallel N1L dimer, Ile6, Leu10, Phe95, and Phe99 constitute a critical hydrophobic patch whereas Arg7/Asp14 and Arg90/Glu103 pairs form complementary electrostatic surfaces, not present in Bcl-XL. The N1L monomer (blue) in this view is related to the blue monomer in A by 90° about a vertical axis. (C) The same view for Bcl-XL showing analogous residues, which are either not hydrophobic or not complementary in charge. BH1–4 domains are colored in magenta (BH4), green (BH3), orange (BH1), and cyan (BH2), as in Figure 1, B and C.