Figure 6.
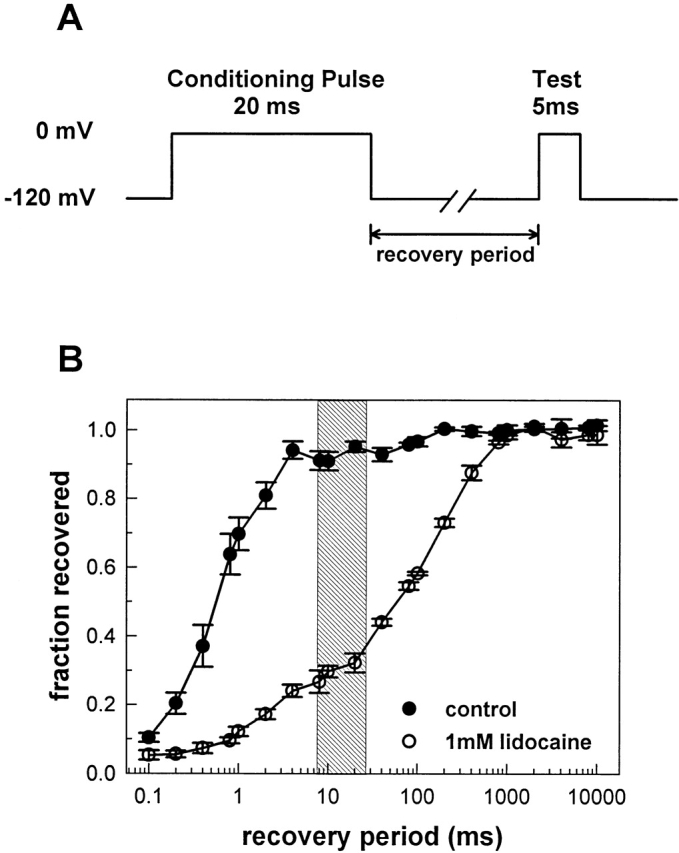
Lidocaine slows the repriming of Na+ channels after brief depolarizations. A two-pulse recovery protocol was used to assess the rate of repriming of F1304C channels after a 20-ms depolarization to 0 mV. The peak current measured during the test pulse was divided by the peak current measured during the conditioning pulse, and plotted as a function of the recovery period. In the absence of lidocaine, the current recovered almost completely within 10 ms, while in the presence of 1.0 mM lidocaine, the time constant of recovery is roughly 100-fold slower. The shaded area indicates the duration of MTS-ET exposure relative to Na+ channel repriming for the protocol shown in Fig. 7 A.
