Fig. 4.
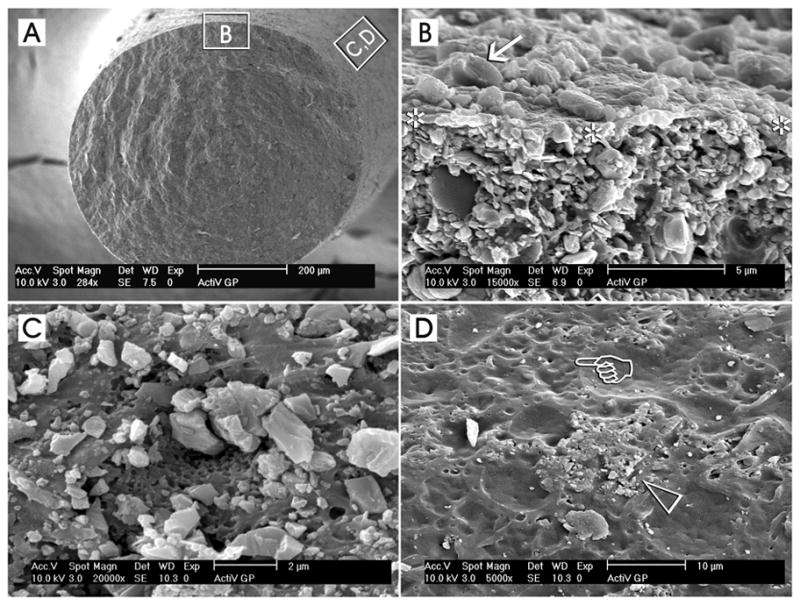
Surface coating of conventional gutta-percha cones with glass ionomer fillers (ActiV GP, Brasseler USA, Savannah, GA) represents an example of a part of the components of a tertiary endodontic monoblock, in which these filler-coated gutta-percha cones are bonded to intraradicular dentin with the use of a glass ionomer root canal sealer. A. A low magnification scanning electron micrograph of a cryofractured ActiV GP gutta-percha cone depicting the representative locations from which the higher magnification micrographs were derived. B. A high magnification interfacial view showing the surface of the fractured gutta-percha cone (between asterisks) with the glass ionomer fillers (arrow) on top of the surface and the filler-dense gutta-percha cone below. C. A high magnification surface view showing a region that is heavily-coated with glass ionomer fillers. The dimensions of these angular fillers ranged from submicrometer to 2 μm in diameter. D. Incomplete or uneven coating of the gutta-percha cone surface could often be observed along different regions of the same coated gutta-percha cone. In this micrograph, the glass ionomer fillers were sparse (open arrowhead) and numerous dimpled, filler-free areas (pointer) could be identified.
