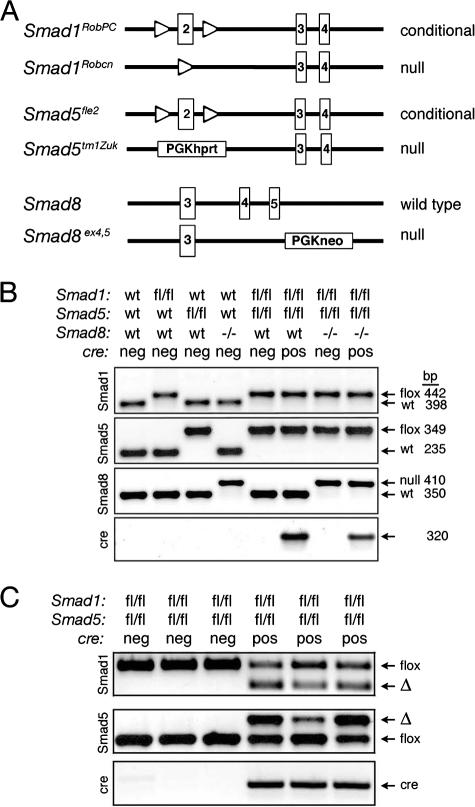
FIG. 1.
Generation of single, double, and triple conditional knockouts. (A) Schematic representation depicting floxed and null alleles for Smad1 (Smad1RobPC and Smad1Robcn, respectively) (53), floxed and null alleles for Smad5 (Smad5fle2 and Smad5tm1Zuk, respectively) (8, 54), and a null allele for Smad8 (Huang et al., submitted). Only a portion of each genomic locus is shown. In both Smad1 and Smad5, loxP sites (open triangles) flank exon 2 (boxed), the first coding exon, which when recombined produces a null allele. The Smad8 null allele deletes exons 4 and 5, which encode the majority of the MH2 domain. PGK phosphoglycerate kinase promoter; hprt, hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase minigene. (B) Genotyping of single, double, and triple control and conditional knockouts by PCR. Each lane represents one mouse of eight possible genotypes. Representative genotyping of genomic tail DNA is shown, with expected sizes of PCR products as indicated. (C) Recombination of floxed (fl) alleles in genomic DNA from isolated granulosa cells of cre-negative (neg) and cre-positive (pos) Smad1flox/flox Smad5flox/flox 21-day-old mice. When crossed to Amhr2cre/+ mice, the deleted allele (Δ) is detected in granulosa cells. Because four independent recombinations have to occur in dKO (Smad1flox/flox Smad5flox/flox Amhr2cre/+) mice, granulosa cells isolated from young mice are mosaic for the deletions and show variable levels of recombination between mice. Each lane represents one mouse.