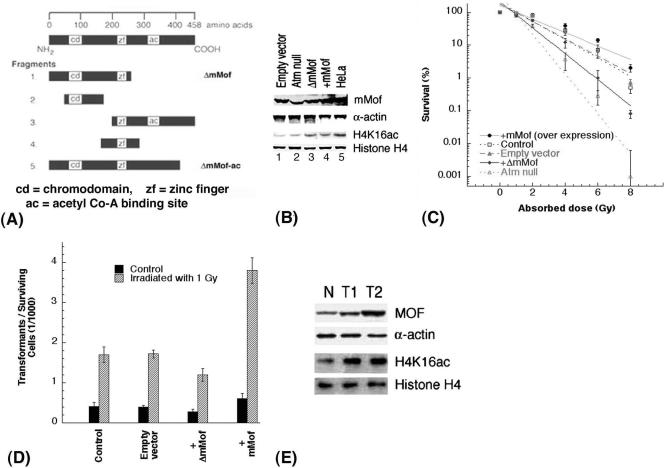
FIG. 7.
The level of mMof protein correlates with cell survival and oncogenic transformation. (A) Strategy for cloning the mMof gene and its domains. mMof protein is denoted at the top with a line representing 458 amino acids. Five different fragments of mMof cDNA encoding full-length mMof protein with three domains (chromodomain region, zinc finger, and acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl Co-A) binding site) are diagrammed. The five different fragments were generated by PCR using specific primers. All clones are drawn to approximate scale. Each fragment is subcloned into pBABE retroviral or pcDNA3.1 vectors. The fragment designated ΔmMof showed dominant-negative activity for cell survival and was used in transformation assays. (B) Western blot analysis to determine the levels of MOF and H4K16ac in mouse 435 and 743 fibroblasts used in the analysis of the assays shown in panels C and D. 435 fibroblasts are mouse cells with wild-type ATM, while 743 fibroblasts are ATM null cells. Lanes 1, 3, and 4 are 435 cells transfected with the described cDNAs. HeLa cell extracts were used as a positive control for detection of MOF protein in mouse cell lines. In panels B and C, the control is 435 mouse fibroblasts. (C) Cell survival of 435 fibroblasts transfected with empty vector, 435 fibroblasts expressing wild-type mMof or ΔmMof, and 743 cells (positive control) determined by colony-forming assay. (D) Transformation incidence following exposure to 1 Gy of gamma rays in 435 (Atm+/+) mouse cells, 435 cells with empty vector, 435 cells with wild-type mMof, and 435 cells with ΔmMof expression. The spontaneous and IR-induced morphological transformation of 435 cells with and without overexpression of mMof was determined as described previously (15). (E) Levels of MOF and H4K16ac in normal thymus (N) and tumor tissues (T1 and T2) from mice. T1 and T2 are samples of two different thymic lymphomas.