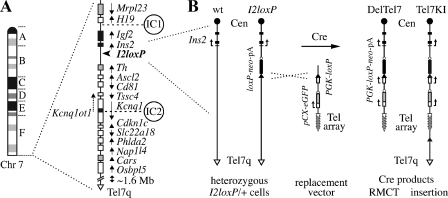
FIG. 1.
Structure of the imprinted domain on distal Chr 7 and strategy for RMCT. (A) Ideogram of Chr 7 (left) and imprinted gene organization (right) in the distal band 7F5. Genes expressed preferentially from the maternal (white) or paternal (black) homologue, as well as known biallelically expressed transcripts (gray), are identified, with arrows showing their transcriptional orientation. Several nonimprinted genes and novel annotated transcripts also map telomeric to the imprinted domain, in a ∼1.6-Mb region of distal Chr 7. The map also shows the positions of the known imprinting centers (IC1 and IC2) and that of the targeted loxP site insertion allele I2loxP used in this study (arrowhead). (B) Close-up maps of the Ins2 region in I2loxP/+ ES cells and two novel alleles. Shown are structures of the wt Ins2 gene and of the Ins2I2loxP allele (I2loxP), as found in G418-sensitive heterozygous I2loxP/+ ES cells (left). The I2loxP allele is the targeted insertion of a loxP site followed by a promoterless neo-pA cassette (loxP-neo-pA) upstream of Ins2. Deletion of the Chr 7 sequences distal of I2loxP by RMCT was achieved by coelectroporation of a Cre recombinase expression vector together with a linear replacement vector (middle) carrying a terminal array of telomere repeats (Tel array), a pCX-eGFP reporter (56), and a PGK promoter-loxP construct (PGK-loxP). Cre recombination in trans between I2loxP on Chr 7 and the vector regenerates an active PGK-loxP-neo-pA-selectable marker and yields the DelTel7 or Tel7KI alleles in G418-resistant derivatives of I2loxP/+ cells (right). In DelTel7, Chr 7 is truncated by RMCT and sequences distal of the I2loxP breakpoint are replaced by the vector from the loxP site to the array of TTAGGG telomeric repeats. Tel7KI is an insertion (pop-in) of the circular replacement vector at I2loxP. Tel7q, Chr 7 distal telomere; Cen, centromere.