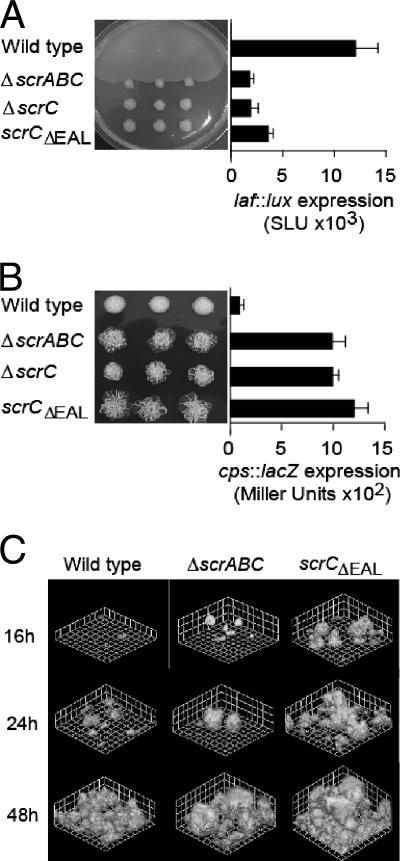
FIG. 1.
Phenotypes of scrABC mutants are determined by the EAL domain of ScrC. (A) Swarming motility of the wild-type (LM5674) and ΔscrABC (LM6567), ΔscrC (LM8021), and scrCΔEAL (LM8022) mutant strains and quantification of laf::lux transcription of the wild-type (LM1017) and ΔscrABC (LM6565), ΔscrC (LM6998), and scrCΔEAL (LM7001) mutant strains. For the swarm plate, three single colonies of each strain were inoculated onto HI swarm plates and incubated overnight. Luminescence was monitored periodically throughout the growth of the strains on the plates, and maximal values of expression are shown. Light (lux) is reported as SLU (total light units per second per milliliter per unit of OD600). (B) Colony morphology of the wild-type (LM5674) and ΔscrABC (LM6567), ΔscrC (LM8021), and scrCΔEAL (LM8022) mutant strains on Congo red medium and quantification of cpsA::lacZ transcription of the wild-type (LM5818) and ΔscrABC (LM6832), ΔscrC (LM6999), and scrCΔEAL (LM7002) mutant strains. For the Congo red plate, colonies were incubated for 1 week at room temperature. β-Galactosidase activity was measured after 16 h of growth on plates and is reported in Miller units. (C) Green fluorescent protein-labeled strains were grown in biofilm flow cell reactors, and scanning confocal laser images were acquired at the indicated times. Grid lines indicate 23.12 μm. Strains: wild type (LM9000), ΔscrABC (LM9001), and scrCΔEAL (LM9002).