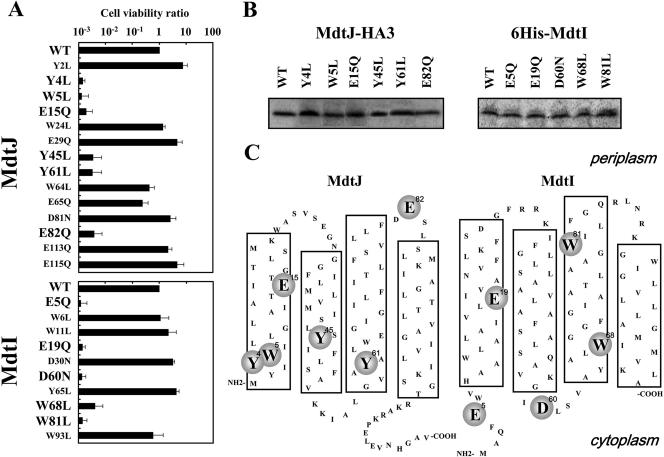
FIG. 5.
Cell viability of various mutants of MdtJ and MdtI. (A) Cell viability of various mutants of MdtJ and MdtI was measured as described in Materials and Methods. Values are means ± SD for three samples. (B) E. coli CAG2242/pUCmdtJ-HA3 and its mutants and E. coli CAG2242/pCA24N-mdtI and its mutants were cultured for 24 h. E. coli CAG2242/pCA24N-mdtI and its mutants were cultured further for 2 h in the presence of 1 mM IPTG. Experiments were repeated twice, and the results were reproducible. The levels of mutated MdtJ and MdtI were evaluated as described in Materials and Methods, using antibodies against the HA tag and the His tag, respectively. (C) Amino acid residues of MdtJ and MdtI involved in relief from spermidine toxicity. Models of secondary structures of proteins were constructed according to the average hydropathy profiles obtained with a hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity plot (Genentyx-Mac, version 10). Putative transmembrane segments are shown in large boxes. Amino acid residues involved in relief from spermidine toxicity are shown in circles.