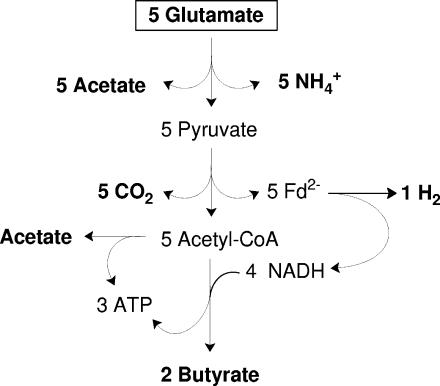
FIG. 1.
Traditional scheme of glutamate fermentation via 3-methylaspartate in C. tetanomorphum. Five pyruvates derived from 5 glutamates are oxidized by 5 ferredoxins to 5 CO2 and 5 acetyl-CoA. The 5 reduced ferredoxins (Fd2−) formed are reoxized by 2 H+ and 4 NAD+, yielding 1 H2 and 4 NADH, respectively. Four of the 5 acetyl-CoA formed are reduced by 4 NADH to 2 butyryl-CoA (see Fig. 2). Three ATP are generated from 2 butyryl-CoA and the remaining 1 acetyl-CoA (see Fig. 5).