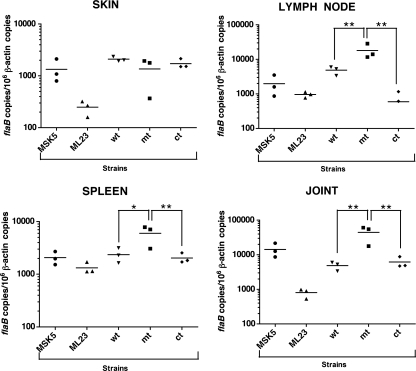
FIG. 4.
Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of the spirochetal burden in mice infected with the BBA64 mt. Groups (n = 3) of 6-week-old C3H/HeN female mice were infected intradermally with B. burgdorferi strains—wt (ML23/pBBE22), mt (MM4/pBBE22), or ct (MM4/pBBE22-bba64+)—at doses ranging logarithmically from 102 to 105 spirochetes per mouse. A similar group (n = 3) of mice was infected with MSK (103) or ML23 (103 and 105) to serve as the positive or negative control, respectively, for infection. Total genomic DNA was isolated from tissues (skin, spleen, lymph node, and joint) using the High Pure PCR template preparation kit, and quantitative real-time PCR was performed. Results for the infection dose of 103/mouse are shown. Numbers of borrelial flaB copies were normalized against total mouse β-actin copies. Only two out of three samples of lymph nodes from mice infected with the ct strain had detectable levels of spirochetal DNA. The asterisks indicate levels of significance as follows: **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05.