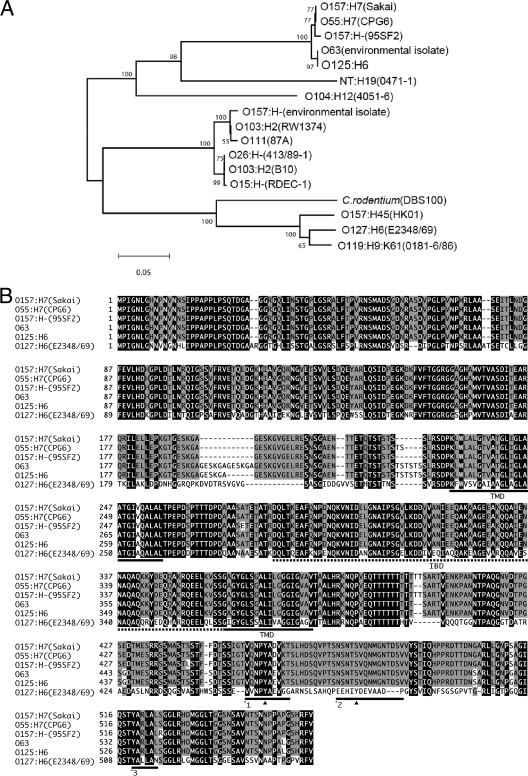
FIG. 2.
A. The phylogenetic relationship of the tir genes from EPEC O125:H6 with selected previously published tir genes. B. The amino acid sequence of Tir proteins of EPEC O125:H6 strain ICC223 was aligned with previously published Tir sequences as described elsewhere (30). The tir genes of amino acid residues identical in all the proteins are indicated in black, and the residues shared by no less than 50% identity within all proteins are gray. The intimin-binding domain and two predicted transmembrane domains are indicated by a dashed line and underlining, respectively. Black triangles indicate the tyrosine residues phosphorylated by a host cell kinase(s). Underlining with *1 indicates the regions containing Y454 that are involved in pedestal formation via the TirEHEC_O157:H7-TccP/EspFu pathway and the alternative TirEPEC_O127:H6-Nck-independent pathway. Underlining with *2 indicates the TirEPEC_O127:H6 Y474 involved in the Nck pedestal formation pathway. The underlining with *3 indicates the region corresponding to the O157 EHEC Tir residues 519 to 524 that may be related to the type III secretion system-dependent secretion efficiency.