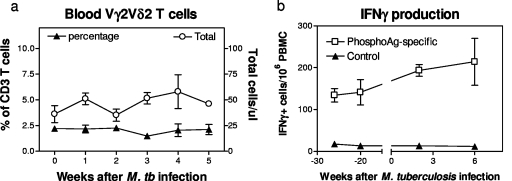
FIG. 2.
There was no significant expansion of Vγ2Vδ2 T cells in the blood circulation after pulmonary M. tuberculosis infection, despite remarkable increases in the numbers of these γδ T cells in lymphoid and nonlymphoid tissues/organs. (a) Percentages (left y axis) and absolute numbers (right y axis) of Vγ2Vδ2 T cells in the blood of four rhesus monkeys after pulmonary M. tuberculosis infection. The slight increase in absolute numbers of Vγ2Vδ2 T cells after the infection was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). (b) Subtle increase in numbers of isopentenyl pyrophosphate-specific IFN-γ-producing Vγ2Vδ2 T cells in the blood of three cynomolgus monkeys after M. tuberculosis infection. Note that circulating Vγ2Vδ2 T cells maintained effector function for IFN-γ production in response to in vitro stimulation with phosphoantigen, but not control glucose, during the early phase of M. tuberculosis infection.