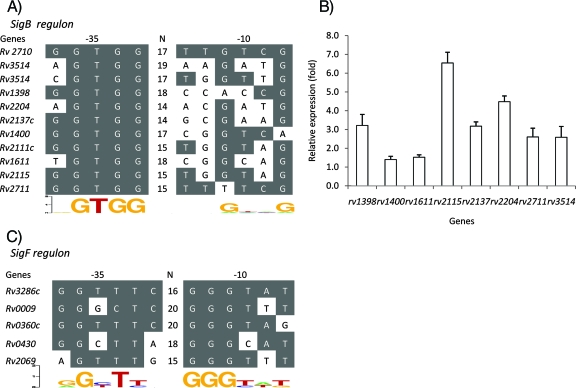
FIG. 2.
Putative promoter consensus recognition sequences of SigB and SigF and confirmation of putative SigB-dependent genes by real-time RT-PCR analysis after sigB induction in the M. tuberculosis sigB KI strain. (A) The SigB putative promoter consensus recognition sequence was identified by analyzing the microarray data from Table 1. Genes found to be upregulated after sigB induction were collected and aligned to determine the sigB promoter consensus sequence. (B) Genes found by microarray to have a putative SigB-dependent promoter were evaluated by real-time RT-PCR for their level of expression before and after sigB KI expression. RNA was obtained 12 h after sigB induction in the M. tuberculosis sigB KI strain. The relative expression values shown are the ratios of postinduction RT-PCR signal normalized to the preinduction levels. The primers used in this experiment are described in Table S1 in the supplemental material. (C) The SigF putative promoter consensus recognition sequence identified in the present study by sigF KI overexpression, as well as those of genes shown to be regulated by SigF in previous studies, were also aligned. The SigF promoter recognition sequence was identified in the 5′ UTR region of the sigC gene (Rv2069). SigB and SigF promoter consensus sequences were derived using weblogo software (http://weblogo.berkeley.edu/logo.cgi).