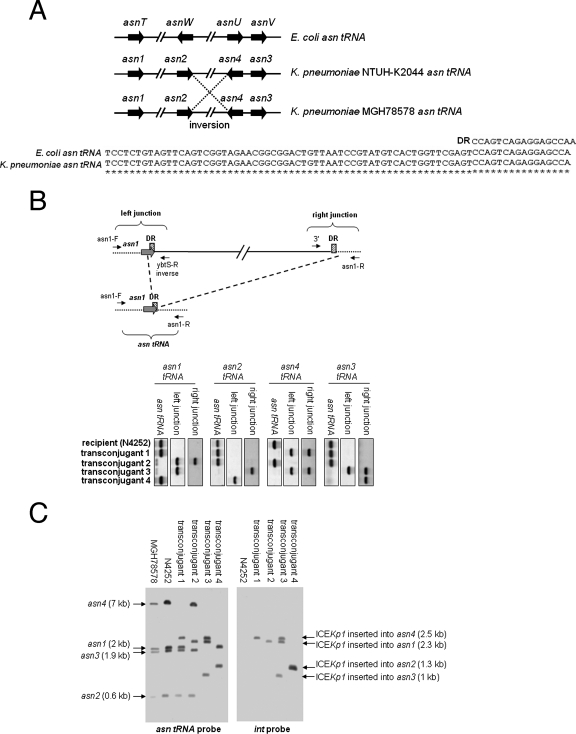
FIG. 6.
Integration of ICEKp1. (A) (Top) Alignment of four asn tRNA genes of E. coli and K. pneumoniae strains NTUH-K2044 and MGH78578. The arrows indicate the locations and orientations of asn tRNA genes. An inversion between the asn2 and asn4 tRNA genes was found in strain MGH78578 (indicated by dashed lines). (Bottom) Alignment of sequences of the 17-bp direct repeat (DR) and asn tRNA genes of E. coli and K. pneumoniae. Asterisks indicate identical nucleotides in the E. coli and K. pneumoniae asn tRNA genes. (B) (Top) Integration of ICEKp1 adjacent to asn tRNA genes (asn1 tRNA, for example). The asn tRNA is indicated by gray arrows, and the cross-hatched box indicates the 17-bp direct repeat (DR). The small arrows indicate the orientations of primers. The asn tRNA gene was detected by primers flanking the asn1 tRNA gene (asn1-F and asn1-R). The left junction of the ICEKp1 insertion was detected by a primer flanking the asn1 tRNA gene combined with a primer in the left end of ICEKp1 (asn1-F and ybtS-R inverse). The right junction of the ICEKp1 insertion was detected by a primer flanking the asn1 tRNA gene combined with a primer in the right end of ICEKp1 (asn1-R and 3′). (Bottom) PCR analysis of the integration site of ICEKp1 in the four N4252 transconjugants. (C) Southern hybridization of EcoRV-digested DNA from various strains with asn tRNA gene (left gel) and int (right gel) probes. The arrows indicate the positions of asn tRNA gene fragments with or without an ICEKp1 insertion.