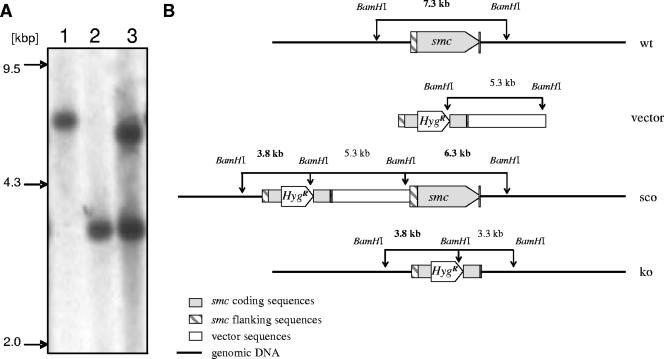
FIG. 1.
Generation of M. smegmatis smc mutant. (A) Southern blot analysis. Genomic DNA from M. smegmatis wild type (lane 1), smc mutant (lane 2), and the smc single-crossover mutant (lane 3) was digested with BamHI and probed with a 685-bp PvuII gene fragment containing the 5′ flanking region of the smc gene. The presence of a single 3.8-kbp fragment in the mutant strain instead of a 7.3-kbp fragment observed in the parental strain demonstrates successful deletion of smc coding sequences. (B) Schematic illustration of the smc locus and the Southern blot strategy. Shown are the genomic organization of the wild type (wt), the knockout vector that contains the deletion allele smc::hyg (vector), the single-crossover genotype (sco), and the mutated genomic smc region in the knockout mutant (ko). Fragments detected by the probe specific for the 5′ flanking region are shown in bold letters.