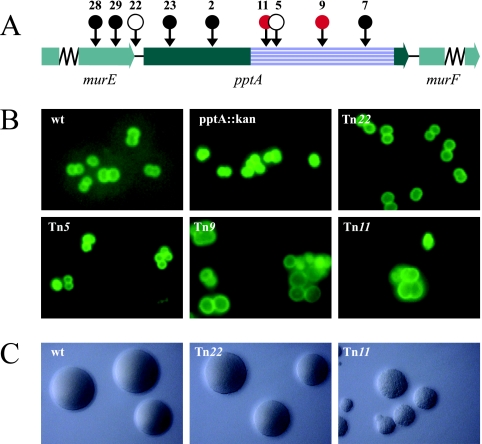
FIG. 1.
Mapping and phenotypic characterization of pptA-linked transposon insertion mutants. (A) Physical map of the gonococcal pptA locus with transposon insertions indicated by circles. •, transposon insertions that could not be recovered in N. gonorrhoeae; ○, insertions with wt growth phenotype. The red circles represent transposon insertions that resulted in aberrant cell septation and coccal morphology. The precise sites of transposon insertion are shown in Fig. S1 in the supplemental material. The striated box defines the Pfam PF00884 sulfatase domain of PptA. (B) Cell septations and coccal morphologies of transposon mutants detected by immunofluorescence microscopy. Gonococci were detected using fluorescein-labeled MAbs (green). (C) Gonococcal colonies on conventional medium showing the different growth phenotypes of transposon mutants. The strains used were wt (N400), pptA::kan (KS9), Tn22 (pptA::Tn22; KS8), Tn5 (pptA::Tn5; KS5), Tn9 (pptA::Tn9; KS6), and Tn11 (pptA::Tn11; KS7).