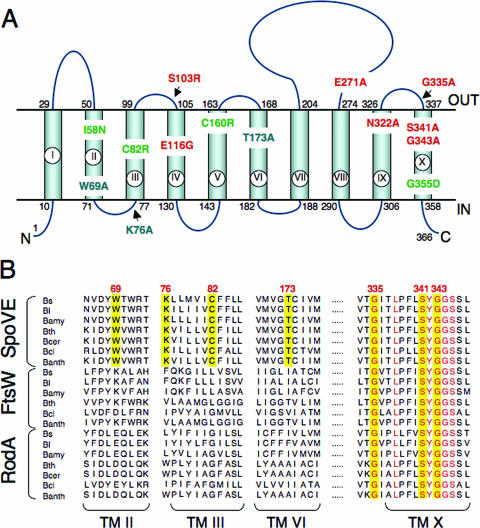
FIG. 4.
Topology model for B. subtilis SpoVE and localization of point mutations. (A) B. subtilis SpoVE membrane topology and the location of SpoVE mutations. The beginning and end of each TM segment (TM I to X) is indicated by the residue number. The model is derived from TopPredII predictions (51) and LacZ and PhoA fusion protein analysis. SpoVE mutations are color coded according to how SpoVE-GFP or SpoVE-YFP mutant proteins carrying the respective mutations accumulate and localize during sporulation: green, have reduced accumulation; red, accumulate and localize; and blue, accumulate but are mislocalized. (B) Partial alignment of SEDS proteins (SpoVE, FtsW, and RodA) from selected members of the genus Bacillus. The alignment shows parts of TM II, III, VI, and X (as represented in panel A for the B. subtilis SpoVE protein) and was obtained using CLUSTAL-W (www.ebi.ac.uk). SpoVE mutations W69A, K76, C82R, and T173A are in residues conserved only among predicted SpoVE proteins, whereas mutations G335A, S341A, and G343A are in conserved residues among the Bacillus SEDS proteins. Residues in the positions corresponding to all six mutations are shown against a yellow background. Other conserved residues in TM X are shown in red. Bs, B. subtilis; Bl, B. licheniformis; Bamy, B. amyloliquefaciens; Bth, B. thuringiensis; Bcer, B. cereus; Bcl, B. clausii; Banth, B. anthracis.