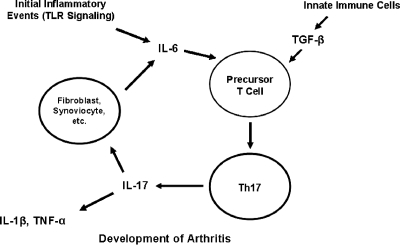
FIG. 1.
Proposed mechanism for the development of Th17 cells and arthritis following infection with B. burgdorferi. Infection with B. burgdorferi stimulates the TLR-mediated release of proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6. IL-6, in combination with endogenous TGF-β, induces the development of Th17 cells from T-cell precursors. Th17 cells produce IL-17, which stimulates the production of other proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β and TNF-α. IL-17 also induces from fibroblasts and synovial cells the production of IL-6, which serves to continue the inflammatory feedback loop. This process may occur until the borrelial load is reduced such that TLR-mediated production of IL-6 is insufficient to influence Th17 cell production.