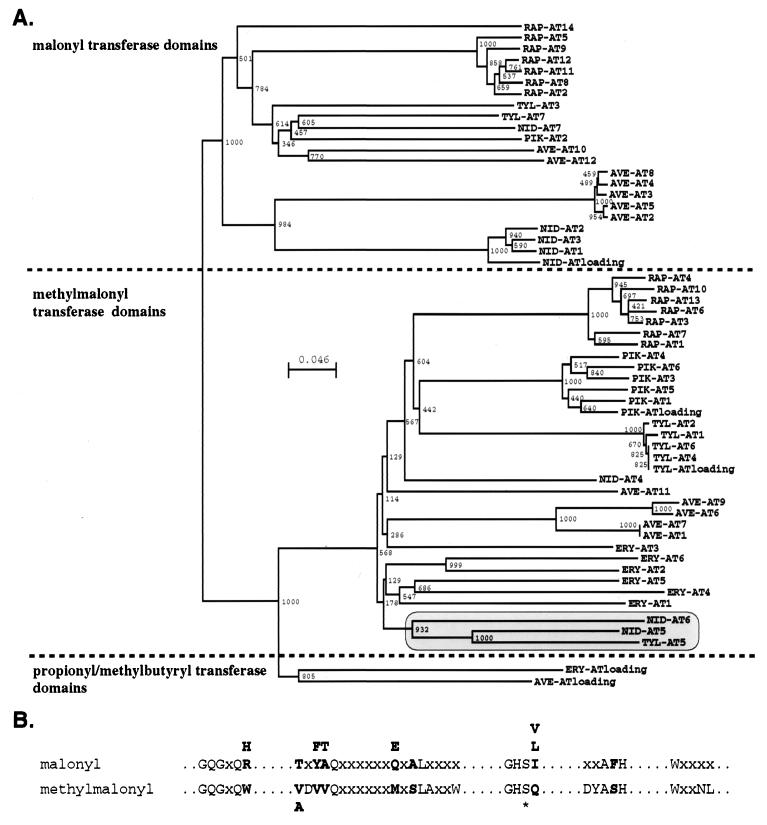
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of acyltransferases. (A) Phylogenetic tree of amino acid sequences of acyltransferase domains from actinomycete type I PKSs showing clustering of malonyl, methylmalony, or propionyl/methylbutyryl loading domain sequence. Domains in the shared box are ethylmalonate (TYL-AT5 and NID-AT5) or hydroxymalonate loading function (NID-AT6). Multiple alignment and phylogenetic analysis using the bootstrapping method were performed by using clustalw. The number of amino acid substitutions is proportional to the length of the horizontal lines. Bootstrap tree is 1,000. AVE, avermectin PKS module; ERY, erythromycin PKS module; NID, niddamycin PKS module; PIK, pikromycin PKS module; RAP, rapamycin PKS module; TYL, tylosin PKS module. (B) Putative consensus sequences of malonyl and methylmalonyl loading domains. All letters shown represent invariant amino acids for the malonyl or methylmalonyl loading domain. Bold letters indicate significant differences between malonyl and methylmalonyl loading domains. The asterisk indicates the serine residue that is linked to the acyl-CoA in the acyl: acyltransferase complex.