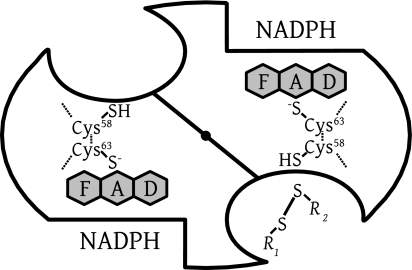
FIG. 3.
Scheme of dimeric human GR representing the active-site geometry of disulfide reductases. There are two identical active sites per homodimeric enzyme. The dimer interface is shown as a diagonal line, with a central filled circle representing the twofold symmetry axis as viewed from above. The reducing equivalents flow from the nicotinamide of NADPH via the flavin to the active-site disulfide, which is reduced to give the catalytic dithiol. Subsequent dithiol-disulfide exchanges lead to the reduction of the substrate GSSG (R1-S-S-R2, with R1 equaling R2). Two binding sites for MB have been identified by crystallography at low resolution, an intersubunit cavity at the twofold axis and a site close to the nicotinamide-binding site (30, 59). In the case of LipDH, the disulfide of lipoamide binds as R1-S-S-R2 at the disulfide site; in the case of TrxR, it is the peripheral disulfide of the other subunit which binds here.