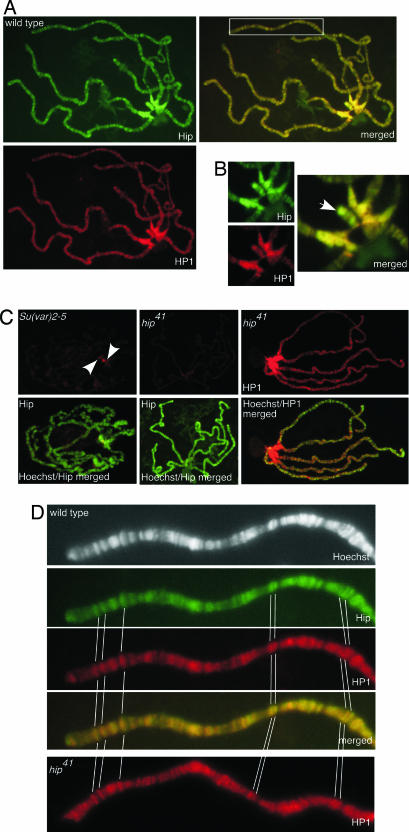
Fig. 3.
Immunolocalization of Hip and HP1 on polytene chromosomes. (A) Both proteins colocalize in the heterochromatic chromocenter (see enlarged detail in B), telomeres, and euchromatic sites (boxed area in merged image is enlarged in D). Third-instar larvae salivary gland chromosomes were immunostained with anti-Hip antibody (green) and anti-HP1 antibody (red). Sites where both proteins colocalize appear yellow in the merged image. (B) Colocalization of Hip and HP1 in the chromocenter and on the fourth chromosome (arrow). (C) Binding of Hip depends on the presence of HP1. Shown are stainings with anti-Hip or anti-HP1 antibody (both in red) on polytene chromosomes counterstained with Hoechst 33258 (green). In Su(var)2-5-deficient larvae almost no HP1 staining could be detected (data not shown). Hip binding to polytene chromosomes is strongly diminished in Su(var)2-5-deficient larvae. A very weak Hip signal remains at the chromocenter (Left, arrowheads). On chromosomes of mutant hip41 homozygous larvae virtually no Hip protein could be detected (Center) whereas the binding of HP1 appears unaffected (Right). (D) An enlarged view of a part of chromosome arm 2L is shown as an example for colocalization of Hip and HP1 at euchromatic sites. In hip41 HP1 binding to euchromatic sites is unchanged. Prominent binding sites are marked.