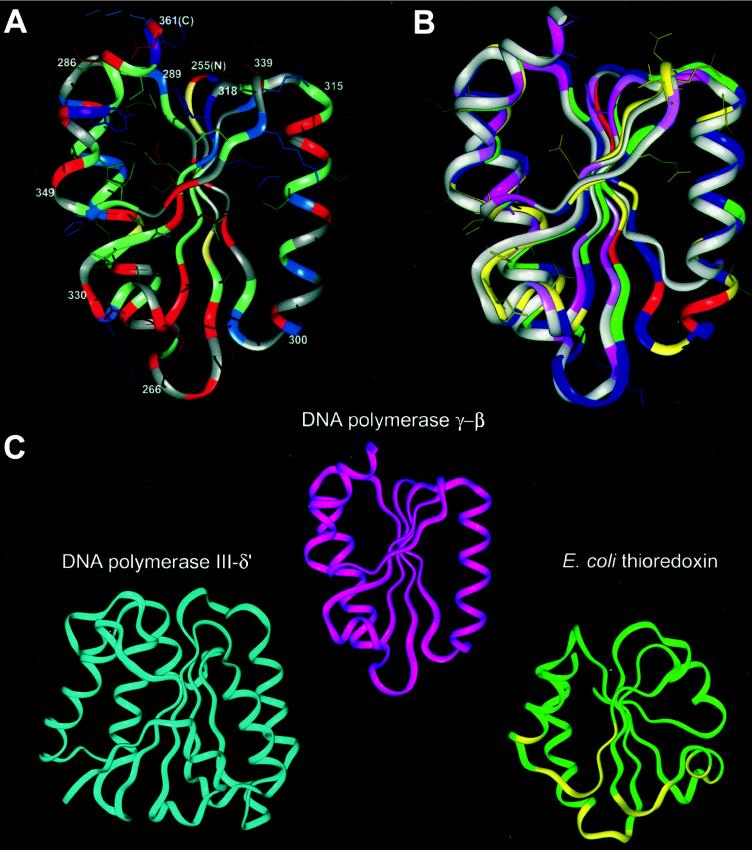
Figure 2.
Structural modeling and comparison of the C-terminal domain of the accessory subunit of Drosophila polγ with other DNA polymerase accessory subunits. (A) Molecular model of the C-terminal domain of Drosophila polγ-β. The main-chain ribbon is shown along with protein side-chain atoms colored according to chemistry: negatively charged residues and derivatives (Asp, Asn, Glu, Gln), red; positively charged residues (His, Lys, Arg), blue; small hydrophobic residues (Leu, Ile, Val, Met), green; large hydrophobic residues (Phe, Tyr, Trp), purple; cysteine, yellow; and other residues (Pro, Ala, Gly, Ser, Thr), gray. The termini of the α-helices and β-strands are numbered according to the Drosophila polγ-β sequence in Fig. 1, with the N and C termini labeled as N and C. (B) Comparison of the structures of the modeled C-terminal domain of Drosophila polγ-β and the C-terminal domain of prolyl-RS, used as a template for the polγ-β model. The main-chain structure of the model, oriented as in A, is shown superimposed onto the anticodon-binding domain of T. thermophilus prolyl-RS. The accessory subunit is colored according to sequence conservation between the Drosophila and human sequences; residues conserved between the two sequences are shown in yellow along with their surface-accessible side chains, conservatively substituted residues are in green, nonconserved residues are in blue, and insertions in the fly sequence relative to the human sequence are in red. (There are no deletions in the fly sequence relative to human.) Conservation is defined as in Fig. 1. The prolyl-RS main-chain ribbon is colored by sequence conservation among the three related aaRSs shown in Fig. 1, with conserved residues in dark pink, similar residues in light pink, and nonconserved residues in grey. (C) Comparison of the structures of the accessory subunit of polγ, the δ′-subunit of E. coli DNA polymerase III, and E. coli thioredoxin. The N-terminal domain of DNA polymerase III δ′ (PDB ID 1a5t; ref. 36) is shown in blue, polγ-β in magenta, and thioredoxin (PDB ID 1t7p, chain B) (40) in green, with thioredoxin residues interacting with the catalytic subunit of T7 DNA polymerase shown in yellow. Optimally similar orientations were produced by using dali (22, 47).