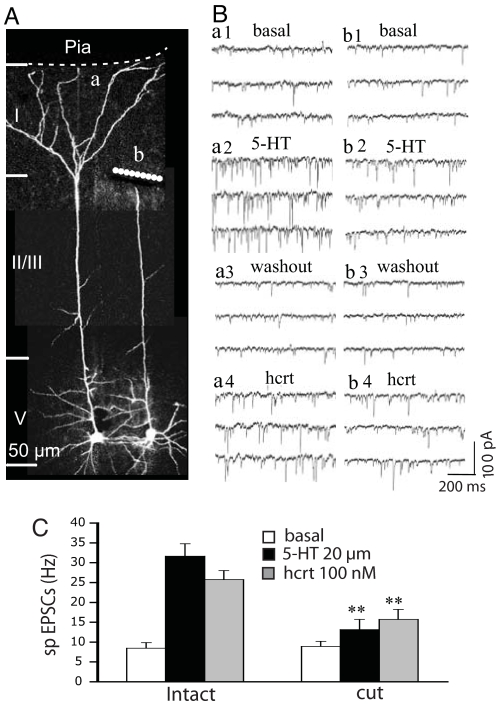
Fig. 1.
5-HT- and hypocretin-induced EPSCs are generated predominantly in the apical tufts of layer V pyramidal cells. (A) 3D Z-stack projections showing a pair of neighboring layer V pyramidal cells, one intact (a) and the other with its apical tuft detached (b). (B) Comparison of effects of 5-HT and hypocretin application on the EPSC response in these two cells; note that the cell with the detached apical tuft has a relatively low EPSC response to 5-HT and hypocretin (b1–4) compared with the intact cell (a1–4). (C) The mean EPSC frequency for eight pairs of cells shows that 5-HT-induced EPSCs are reduced by 80% and hypocretin-induced EPSCs are reduced by 60% in the group with detached apical tufts (n = 8; P < 0.001), confirming that a major proportion of EPSCs induced by 5-HT and hypocretin in layer V pyramidal cell in the mPFC are generated in the apical tuft. Note: dashed line depicts location of the pial membrane, which forms the medial border of mPFC; layers I–V are demarcated by horizontal lines.