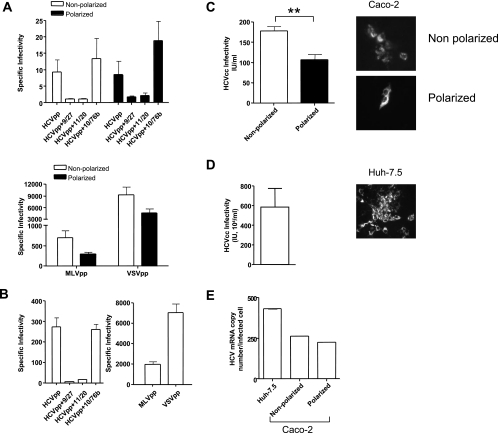
FIG. 5.
HCV entry and infection of polarized cells. (A) HCVpp infection of nonpolarized (white bars) or polarized (black bars) Caco-2 cells in the presence or absence of neutralizing anti-HCV E2 MAbs 9/27 and 11/20 and control anti-HIV gp120 MAb 10/76b. MLVpp and VSVpp infection of nonpolarized (white bars) or polarized (black bars) Caco-2 cells is shown. Data are expressed as specific infectivity where the ratio of luciferase activity for HCVpp or control MLV/VSVpp to Env− particles is shown. (B) HCVpp, MLVpp, and VSVpp infection of Huh-7.5 hepatoma cells seeded under conditions optimized for infection (see Materials and Methods). (C) HCVcc JFH-1 infection of nonpolarized (white bar) and polarized (black bar) Caco-2 cells. (D) HCVcc JFH-1 infection of Huh-7.5 hepatoma cells. Infected cells were visualized after 96 h by staining for NS5A expression, and the number of infected cells was defined as the number of infectious units per milliliter. (E) HCV copy numbers in JFH-1-infected Caco-2 and Huh-7.5 cells were determined by real-time PCR with an endogenous control (the gene for GAPDH) to quantify the HCV copy number relative to cellular RNA (ΔCt). HCV RNA levels were normalized to the number of NS5A+ cells. **, P < 0.001 (t test).