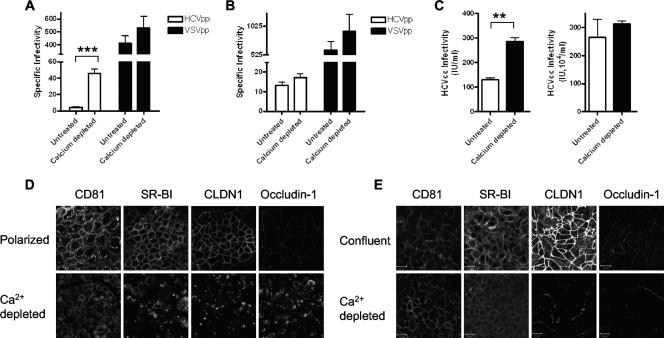
FIG. 7.
Effect of disrupting TJs on HCV entry and infection. (A) Caco-2 cells were grown until polarized. To investigate the effect of disrupting TJs on HCV entry, cells were depleted of calcium by incubation with calcium-free medium supplemented with 0.5 mM EGTA for 16 h. Treated and untreated cells were tested for the ability to support infection with HCVpp (white bars) or VSVpp (black bars). (B) Untreated and calcium-depleted Huh-7.5 cells were tested for the ability to support infection with HCVpp (white bars) or VSVpp (black bars). Data are expressed as specific infectivity where the ratio of luciferase activity for HCVpp or control VSVpp to Env− particles is shown. (C) Effect of depleting polarized Caco-2 (left side) and Huh-7.5 (right side) cells of calcium on JFH-1 infectivity. Infected cells were visualized after 96 h by staining for NS5A expression, and the number of infected cells was defined as the number of infectious units per milliliter. Confocal imaging of CD81, SR-BI, CLDN1, and occludin 1 in untreated polarized and depleted Caco-2 (D) and nonpolarized Huh-7.5 (E) cells. The scale bars represent 20 μm. **, P < 0.001; ***, P < 0.0001.