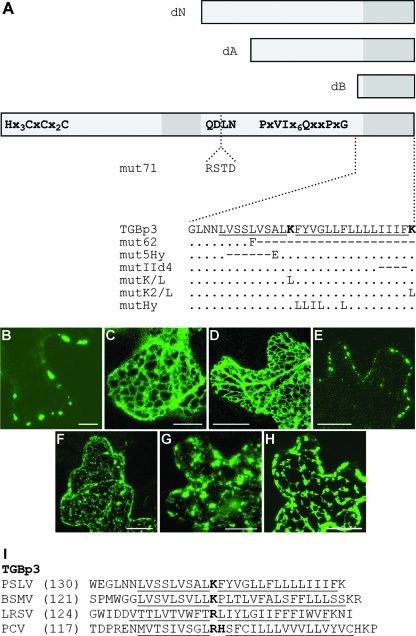
FIG. 5.
Construction and subcellular localization of PSLV TGBp3 mutants. (A) Schematic representation of TGBp3 and its mutants. The box represents the TGBp3 sequence. Conserved amino acid motifs are shown. Two hydrophobic sequence segments are shown as dark-gray boxes. The boxes above the protein scheme show the N-terminally truncated mutants dN, dA, and dB. The insertion of four amino acid residues interrupting the conserved tetrapeptide QDLN in mut71 is shown. Below the protein scheme, the sequences of the C-terminal hydrophobic segment and its mutants are shown. In the native sequence, the hydrophobic regions are underlined, and the positively charged Lys residues are shown in bold. For the mutants, amino acid substitutions are shown. The dots indicate identical residues. The dashes indicate deletions. (B to H) Confocal laser-scanning microscopy of N. benthamiana epidermal cells transiently expressing fluorescent fusions of PSLV TGBp3 and its mutants after microprojectile bombardment. (B) GFP-18K; (C) GFP-18KdA; (D) GFP-18KdB; (E) GFP-18KdN; (F) GFP-18Kmut5Hy; (G) GFP-18KIId4 18K-GFP; (H) 18K-GFP. All images were constructed by the superposition of a series of confocal optical sections. Scale bars = 20 μm (C, D, and E) and 10 μm (the other panels). (I) Amino acid sequences of the C termini of TGBp3 encoded by three hordeiviruses (Barley stripe mosaic virus [BSMV], PSLV, and Lychnis ringspot virus [LRSV]) and Peanut clump virus (PCV; genus Pecluvirus). Hydrophobic sequences are underlined, and interrupting positively charged residues are shown in bold. The numbers in parentheses are the numbers of residues in the protein sequences not shown in the alignment.