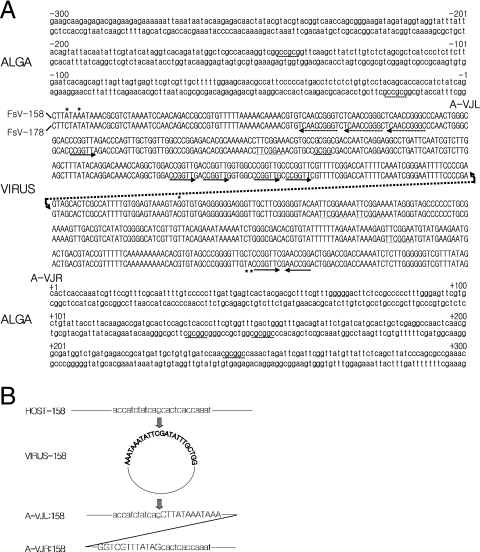
FIG. 4.
(A) Sequence of the host and FsV-158 and FsV-178 around the site of integration. The sequences are numbered from −300 to +300, with zero representing the IS-A. The regions containing virus DNA sequence are represented in uppercase letters while host DNA sequence is in lowercase. The repeated sequences, described in the text, are underlined. The right arrow marks the virus sequence CCGGTT while the left arrow marks the reverse complement, AACCGG. An asterisk marks bases which vary between virus sequences. The virus integration sites and unoccupied host sites are aligned, and the FsV-158 is represented by the upper line of the couplet, and FsV-178 is represented by the lower. The conserved GC dinucleotide present in the viral genome and host integration sites is shown resulting in junctions A-VJL and A-VJR. (B). Detailed sequence representation in the close vicinity of IS-V and IS-A and the junctions created upon integration. Uppercase and lowercase letters are as described for panel A.