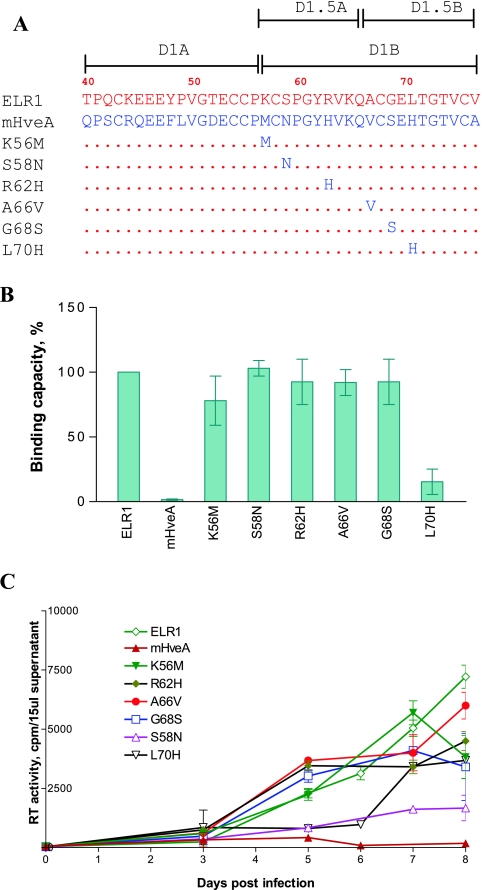
FIG. 4.
Mapping of CRD1 residues critical for ELR1 function by loss-of-function analyses of point mutations converting ELR1 to murine HveA amino acids. (A) Schematic representation of the series of point mutations constructed by substituting the indicated amino acids of ELR1 CRD1 with the corresponding amino acid from the murine HveA CRD1 sequence. All point mutations were made in the E1M2M3M4 chimeric receptor to isolate the equine CRD1 contributions to function. The names and C-terminal CRD1 sequences of the various receptor mutants derived from E1M2M3M4 are shown. Amino acids of ELR1 and mHveA are in red and blue letters, respectively. Numbers indicate positions of amino acids in the predicted protein sequence of full-length ELR1. Dots in the mutant receptor sequences indicate identical amino acids to ELR1. (B) EIAV gp90 binding capacity of each receptor mutant expressed as a percentage of ELR1 binding in the cell-cell binding assay. (C) EIAV replication in Cf2Th cells transduced by the indicated chimeric receptor protein constructs, as described for Fig. 2.