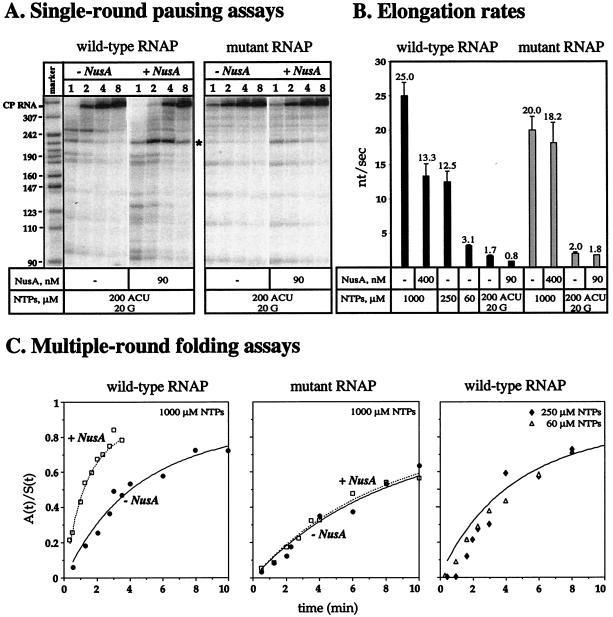
Figure 3.
(A) Synthesis of CP RNA by wild-type and mutant E. coli RNAP in the absence or in the presence of 90 nM NusA. The darkness of the bands reflects the dwell time at specific pausing sites. Asterisk indicates the pausing site at nucleotide U55 (225th position in the CP RNA). (B) Elongation rates of wild-type (solid bars) and mutant (shaded bars) E. coli RNAP were determined from single-round transcription assays on CP RNA template at the concentrations of NTP and NusA indicated below the bar graph. (C) Folding of CP RNA during transcription by 0.2 μM wild-type (Left) and mutant (Right) RNAP in the absence (●) and presence (□) of 0.4 μM NusA or by 0.2 μM wild-type enzyme at 0.06 mM (▵), 0.25 mM (♦), and 1 mM (curve fit) NTP. The synthesis of CP RNA by the E. coli RNAP is nonlinear and is best fit by a transcription rate (ks) of 0.046 ± 0.016 μM/min and an association constant (K) of (0.20 ± 0.08) × 10−3 μM−1 according to Eq. 2. The folding rates are determined by the cleavage of a pre-tRNA substrate.