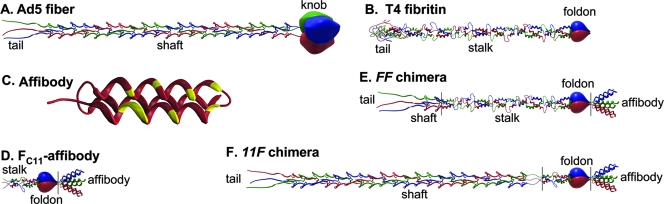
FIG. 1.
Design of Her2-targeted Ad fiber protein. (A) The Ad5 fiber is a homotrimer whose tail anchors it within the Ad virion. The globular knob domain initiates the trimerization of individual subunits by aligning them and also makes viral infection possible by binding to Ad5 natural receptor, CAR. The fibrous shaft domain consists of 21 pseudorepeats that form a characteristic β-spiral structure. (B) Similar to the Ad5 fiber, the fibritin is a homotrimer that has the tail, the stalk, and the foldon domains. The stalk connects the globular tail and foldon and consists of 13 α-helical coiled coils connected with loops. The carboxy-terminal foldon is a very small (30 amino acids) and stable trimerization motif. (C) The affibody is a 58-amino-acid-long artificially designed ligand derived from Staphylococcus protein A. An array of 13 amino acids, which is engrafted into two of the three α-helices of an affibody by combinatorial randomization, forms a target-binding site (shown with yellow). (D) The Fc11-affibody protein is designed as a replacement for the Ad5 fiber knob domain. It consists of the foldon and the two preceding coiled coils of the fibritin's stalk. Within this molecule, the foldon holds the three subunits of the chimera together, while the affibody binds to the target receptor. The FF-type (E) and 11F-type (F) fiber-fibritin-affibody chimeras are designed as targeted equivalents of the Ad5 fiber. They are similar in that each contains three structural elements—the affibody ligand (or the parental dZ scaffold) and the fragments of both the fiber and the fibritin. The FF-type chimera incorporates the tail and the first two pseudorepeats of the Ad5 fiber shaft fused with the fragment of fibritin truncated at the sixth coiled coil of the stalk. The 11F-type chimera resembles the structure of the fiber more closely, as it contains two complete domains of the fiber, the tail and the shaft. The flexible linker sequence, which connects the shaft and knob domains in the wt fiber, links the β-spiral shaft to the α-helical segment of the fibritin, thus facilitating this structural transition within the 11F protein. Vertical black lines in panels D, E, and F indicate the fusion points between individual components of the chimeric proteins.