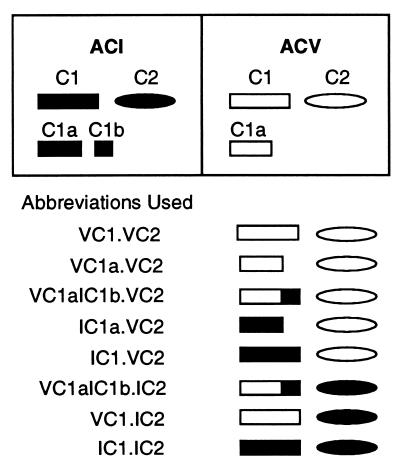
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the abbreviations used to describe the various forms of AC derived by mixing the cytosolic C1 or C1a or chimeric C1 regions with C2 domains of either ACV or ACI. The various domains of ACI (black) and ACV (white) are represented in the boxes. The amino acid residues encompassing the domains in bovine ACI are as follows: C1, 236–607; C1a, 236–471; C1b, 472–607; C2, 809–1,133. In canine ACV, the domains shown comprise the following amino acid residues: C1, 322–683; C1a, 322–571; C2, 933–1,184. In the list of abbreviations, the roman numeral preceding the C1 or C2 domains and their subregions denote the AC isoform from which that particular region is derived.