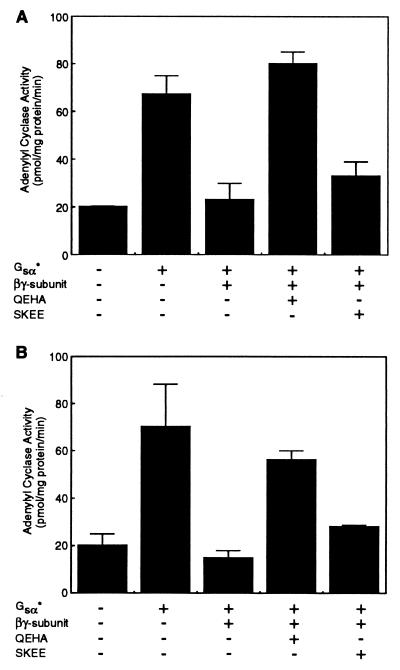
Figure 4.
The peptide QEHA corresponding to amino acid residues 956–982 in ACII attenuates the ability of βγ subunits to inhibit AC activity. (A) IC1a⋅VC2 form of AC was stimulated by Gsα* (80 nM). The ability of βγ subunits (200 nM) to inhibit Gsα*-stimulated activity was monitored in the presence and absence of 200 nM each of the peptides QEHA and SKEE; peptide SKEE corresponds to residues 1,000–1,026 in ACIII, the cognate region of peptide QEHA in ACII. The mean ± SEM (n = 3 experiments) are shown. (B) Same as A except that the VC1aIC1b·IC2 form of AC was used. The mean ± SEM (n = 3 experiments) is presented.