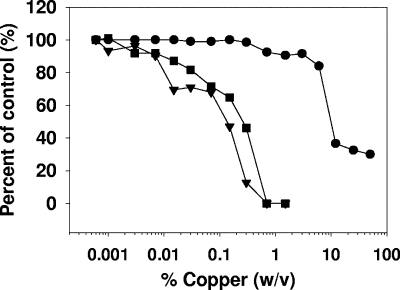
FIG. 2.
Inhibition of cell-associated HIV-1 infectivity by cupric and cuprous oxide powder mix. H9+ cells, which were exposed for 2 h to different concentrations of copper powder mix, were cocultured with attached cMAGI target cells for 3 h, before being thoroughly removed. The cMAGI cells were then cultured for 3 days, and the number of cells infected with HIV-1 was then determined (▪). In addition, the supernatants containing HIV virions that budded out from the H9+ cells during the period when these cells were exposed to the copper were added to uninfected cMAGI cells. After 3 days of incubation, the number of infected cMAGI cells was determined (▾). The viabilities of the H9+ cells exposed to the various copper concentrations are also shown (•). Cell viability is expressed as a percentage of a control using untreated cells. The data shown are the average of duplicate samples. The differences between the duplicate samples were not more than 5%.