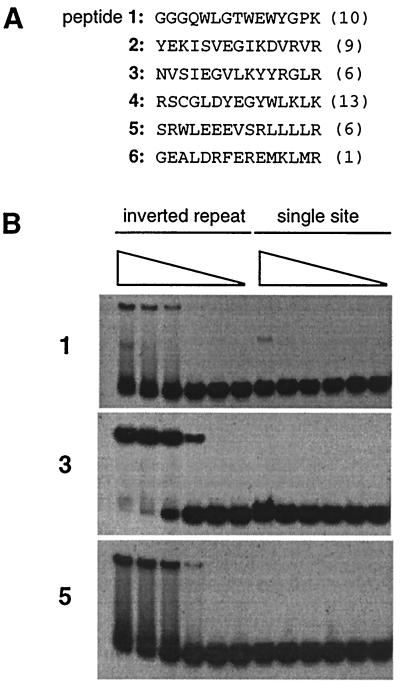
Figure 2.
(A) Sequences of peptide extensions isolated from the initial selection. Numbers in parentheses give the frequency of occurrences among the 45 clones sequenced. The clones for peptide 2 included a Glu-21-to-Asp mutation in the zinc finger region that may have been partially responsible for the affinity of this peptide. (B) Gel mobility-shift assays using purified fusion peptides 1, 3, and 5. Protein (2.5 μM, 250 nM, 25 nM, 2.5 nM, 250 pM, and no protein) was incubated with DNA containing either an inverted repeat of Zif12 sites or a single Zif12 site and then electrophoresed through native polyacrylamide gels. The reduced mobility of the inverted repeat probe in the presence of protein indicates the formation of protein–DNA complexes. Similar results were obtained with fusion peptides 2 and 6, but data are not shown because these peptides were not studied further. Binding of peptide 4, also not shown, appeared to depend on disulfide bond formation, and this peptide was not pursued further.