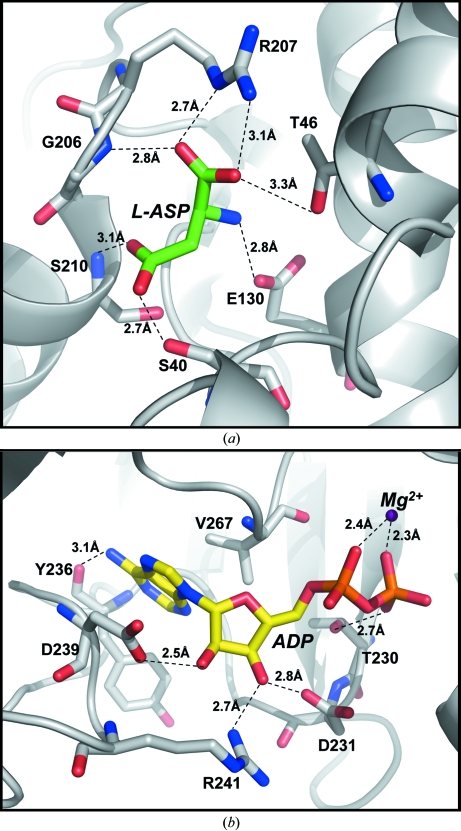
Figure 4.
Expansion of the mjAK structure showing the substrate-binding sites. (a) The amino-acid binding site, with each interaction <3.4 Å annotated. The α-carboxyl group of l-aspartate (L-ASP) forms an ion pair with Arg207 and a hydrogen bond with the backbone amide of Gly206 and the side chain of Thr46. The α-amino group of l-aspartate interacts electrostatically with the carboxyl group of Glu130. The β-carboxyl group, the phosphoryl acceptor, forms hydrogen bonds with the backbone amide of Ser210 and the side chain of Ser40. (b) The nucleotide-binding site. The divalent cation, Mg2+, forms a bridge between the α- and β-phosphate groups of ADP. The ribose moiety is bound by interactions with the side chains of Asp231, Asp239 and Arg241, while the adenine ring is positioned through hydrophobic interactions with Val267 as well as a hydrogen bond to the hydroxyl group of Tyr236.