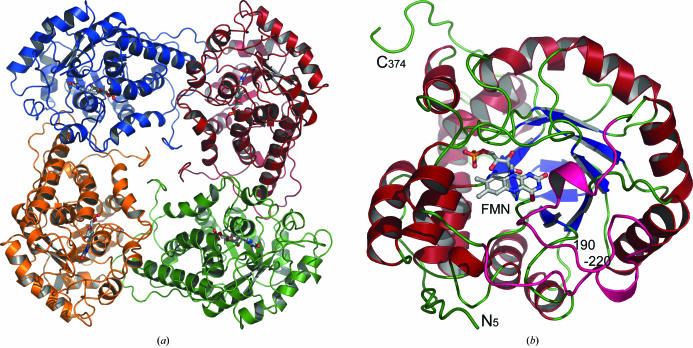
Figure 1.
Overall structure of the A. viridans l-lactate oxidase. (a) The l-lactate oxidase tetramer, describing half of the asymmetric unit. The C-terminus of the monomer folds to fill the central channel within the biologically relevant tetramer. (b) The monomer structure viewed from the C-terminal side of the β-barrel and into the active site where the FMN cofactor is located. The active site is located on the tip of the β-barrel and residues 190–220 (in pink) form a lid over the active site.