Abstract
In this study, we have investigated the role of the cannabinoid CB2 (CB2) receptor in an in vivo mouse model of hepatic ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. In addition, we have assessed the role of the CB2 receptor in TNF-α-induced ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression in human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (HLSECs) and in the adhesion of human neutrophils to HLSECs in vitro. The potent CB2 receptor agonist HU-308, given prior to the induction of I/R, significantly attenuated the extent of liver damage (measured by serum alanine aminotransferase and lactate dehydrogenase) and decreased serum and tissue TNF-α, MIP-1α, and MIP-2 levels, tissue lipid peroxidation, neutrophil infiltration, DNA fragmentation, and caspase 3 activity. The protective effect of HU-308 against liver damage was also preserved when given right after the ischemic episode. HU-308 also attenuated the TNF-α-induced ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression in HLSECs, which expressed CB2 receptors, and the adhesion of human neutrophils to HLSECs in vitro. These findings suggest that selective CB2 receptor agonists may represent a novel, protective strategy against I/R injury by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and apoptosis.
Keywords: endothelial activation, adhesion, inflammation, TNF-α
INTRODUCTION
Ischemia reperfusion (I/R) is the major mechanism of organ injury during myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary bypass surgery, and organ transplantation. The devastating effects of I/R arise from the acute generation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species following reoxygenation, which inflict direct tissue injury and initiate a chain of deleterious cellular responses leading to inflammation, cell death, and eventually, organ failure (reviewed in refs. [1–7]).
The endocannabinoid system is a novel target in various inflammatory, metabolic, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and liver disorders (reviewed in refs. [8–15]). The synthetic and natural ligands (the latter called endocannabinoids: arachidonoyl ethanolamide or anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol) of cannabinoid (CB) receptors exert various anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective [16–18] effects by inhibiting the generation and release of proinflammatory cytokines and mediators (reviewed in refs. [14, 19–21]). Two CB receptors have been identified by molecular cloning to date: the CB1 receptor, which is highly expressed in the brain [22] but is also present in peripheral tissues, including the heart [23, 24], vascular tissues [25, 26], and liver [27–30], and the CB2 receptor, previously thought to be expressed primarily in immune and hematopoietic cells (ref. [31]; reviewed in ref. [14]). More recent studies have also identified CB2 receptors in brain [32], myocardium [33], cardiomyoblasts [33, 34], and endothelial cells of various origins [35–38].
There is limited and conflicting information about the role of CB receptor activation in cell-protective mechanisms against tissue damage (including I/R) in the heart and brain (reviewed in refs. [14, 19, 20, 39–41]). Most published studies were performed by using ex vivo models (e.g., isolated perfused hearts), where the role of important interactions of activated endothelium and leukocytes and other immunomodulatory effects of CBs could not be evaluated, and used nonspecific ligands for CB2 receptors (reviewed in refs. [14, 39–42]).
In the present study, we have used a potent and selective CB2 receptor agonist HU-308 [43] to reveal the role of CB2 receptors in an in vivo model of liver ischemia reperfusion and in TNF-α-induced ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression in human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (HLSECs) and adhesion of human neutrophils to HLSECs in vitro.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals
All animal experiments conformed to National Institutes of Health (NIH) guidelines and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA; Bethesda, MD, USA). C57Bl/6J mice were obtained from The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME, USA).
Hepatic I/R protocol
Mice were anesthetized with pentobarbital (65 mg/kg i.p.). A midline laparotomy incision was performed to expose the liver. The hepatic artery and the portal vein were clamped using microaneurysm clamps. This model results in a segmental (70%), hepatic ischemia. This method of partial ischemia prevents mesenteric, venous congestion by allowing portal decompression throughout the right and caudate lobes of the liver, which was kept moist at 37°C with gauze soaked in 0.9% saline. Body temperature was maintained at 37°C using a thermoregulatory heating blanket and monitoring of body temperature with a rectal temperature probe. Sham surgeries were identical, except that hepatic blood flow was not reduced with a microaneurysm clamp, and animals were killed 3 h or 25 h following the surgery, respectively. The duration of hepatic ischemia was 60 min in all experiments, after which the microaneurysm clamps were removed. The duration of the reperfusion was 120 min or 24 h, as indicated. After reperfusion, blood was collected, and liver samples were removed, weighed, and snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen for determining biochemical parameters or fixed in 4% buffered formalin for histopathological evaluation.
Drugs
AM251 and AM630 were from Tocris (Baldwin, MO, USA), HU-308 was from Cayman Europe (Estonia). All drugs were dissolved in vehicle solution (one drop of Tween-80 in 3 ml 2.5% DMSO in saline) and injected i.p. 60 min prior the occlusion of the hepatic artery and the portal vein. In a separate set of experiments, HU-308 (10 mg/kg) was injected into the femoral vein right before the reocclusion. Vehicle solution was used in control experiments. For cell culture experiments, all lipid-soluble drugs were dissolved in DMSO. All chemicals were from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA), except where it was mentioned.
Plasma alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels
The concentrations of ALT and LDH, indicators of liver and tissue damage, were measured in plasma samples using a clinical chemistry analyzer system (Prochem-V, Drew Scientific, Oxford, CT, USA), as described [44].
Lipid peroxidation
Malondialdehyde (MDA) formation was used to quantify the lipid peroxidation in tissues and measured as thiobarbituric acid-reactive material, as described [44, 45]. Briefly, tissues were homogenized (100 mg/ml) in 1.15% KCl buffer. Homogenates (200 μl) were then added to a reaction mixture consisting of 1.5 ml 0.8% thiobarbituric acid, 200 μl 8.1% SDS, 1.5 ml 20% acetic acid (pH 3.5), and 600 μl distilled H2O and heated at 90°C for 45 min. After cooling to room temperature, the samples were cleared by centrifugation (10,000 g, 10 min), and their absorbance at 532 nm (A532) was measured with 1,1,3,3-tetramethoxypropane as an external standard. The level of lipid peroxides was expressed as nmol MDA/mg protein.
Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity
MPO activity was measured as described previously [44, 45]. Briefly, liver samples were homogenized (50 mg/ml) in 0.5% hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide in 10 mM 3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid and centrifuged to separate the supernatant. An aliquot of the supernatant was mixed with a solution of 1.6 mM tetramethylbenzidine and 1 mM hydrogen peroxide. Activity was measured spectrophotometrically as the change in A650 at 37°C using a Spectramax microplate reader (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). MPO activity was expressed as mU/mg protein. Protein content was determined with the DC protein assay (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA).
Levels and expression of TNF-α, MIP-1α, MIP-2, and ICAM-1
The levels of the inflammatory cytokine TNF-α and the chemokines MIP-1α and MIP-2 in plasma or homogenized liver tissue were determined using commercially available ELISA (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA), according to the manufacturer’s protocol, as described previously [44, 45].
DNA fragmentation assay
The assay was based on measuring the amount of mono- and oligonucleosomes in the cytoplasmic fraction of tissue extracts using the commercially available kit (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Germany), according to the manufacturer’s instructions, as described [33].
Caspase 3 activity
Caspase 3 activity in the tissue extracts was determined by using the commercially available kit (Chemicon, El Segundo, CA, USA). In brief, the assay is based on measuring the amount of chromophore p-nitroaniline (pNA) liberated from the labeled substrate Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-pNA at 405 nM as described [33].
Cell culture
HLSECs were obtained from Cell Systems (Kirkland, WA, USA) and grown in CSC-complete growth medium, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Cells were grown in 0.2% gelatin-coated 100 mm cell culture dishes and used within three to six passages. Polymorphonuclear neutrophil leukocytes (PMN) were isolated from whole blood obtained from a healthy volunteer (NIH Clinical Center, Bethesda, MD, USA) using Percol (GE Biosciences, Piscataway, NJ, USA) density gradient solution.
RT-PCR analysis for CB2 receptor gene expression was performed from HLSECs, as described previously [33].
Cell surface ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression
Cell surface expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 was measured by in situ ELISA, as described [44]. In brief, HLSECs were grown in 96-well plates coated with 0.2% gelatin. The cells were treated with TNF-α (50 ng/ml) ± HU-308 (0–4 μM) for 4 h. In some experiments, the cells were treated with HU-308 (3 μM), AM251, or AM630, each used at the concentration of 1 μM for 1 h, followed by incubation with TNF-α for 4 h (indicated drugs were also present during TNF-α exposure). Then, cells were washed with PBS and fixed in 4% formaldehyde (pH 7.4) and blocked with PBS containing 1% BSA containing 100 mM glycine for 2 h at 4°C. The fixed monolayer was probed with anti-human ICAM-1 or VCAM-1 mAb (R&D Systems) for 1 h at 37°C and incubated with peroxidase-coupled anti-mouse IgG (1:5000, Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA) for 1 h at 37°C. Following washing, cells were incubated with 100 μl developing substrate solution (3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine, Sigma Chemical Co.) for 10 min, and the reaction was terminated with 50 μl 2 N H2SO4, measured as A450. Each treatment was performed in triplicate, and the experiments were repeated three times.
PMN—endothelial cell adhesion
Neutrophil adhesion to endothelial cells was performed as described [44]. In brief, HLSECs were grown to confluence in 24-well plates and treated with TNF-α ± HU-308 or pretreated with CB1/CB2 antagonists followed by treatment with TNF-α/HU-308 as described above. Then, PMN were labeled with 2.5 μM Calcein-AM (Molecular Probes-Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) for 1 h at 37°C in RPMI 1640 containing 1% FBS. HLSECs were washed twice with HLSEC basal medium and covered with 400 μl HLSEC basal medium. Then, 5 × 104/100 μl-labeled PMN cells were added to HLSECs and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. After incubation, the monolayer was washed carefully with PBS to remove the unbound PMN. The adherent PMN were documented by an Olympus IX 81 fluorescent microscope using a 20× objective (Opelco, Dulles, VA, USA). Three fields were captured per experimental condition. Individual treatments were preformed in duplicate, and the entire set of experiments was repeated twice. The number of adherent PMN cells was counted using NIH Image J software, and the values were expressed as PMN adhered/field.
Histological analysis of liver samples
Liver samples were fixed in 4% buffered formalin. After embedding and cutting 5 μm slices, all sections were stained with H&E. MPO staining of neutrophils was done by using anti-MPO antibody, according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Zymed Lab., San Francisco, CA, USA), and samples were contrastained with nuclear fast red. Histological evaluation was performed in a blinded manner.
Statistical analysis
Results are presented as means ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keuls multiple comparisons post hoc analysis was calculated using the GraphPad Prism 4 package (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). P < 0.05 was considered significant.
RESULTS
CB2 agonist attenuates markers of I/R-induced tissue injury (ALT and LDH), lipid peroxidation, and MPO activity
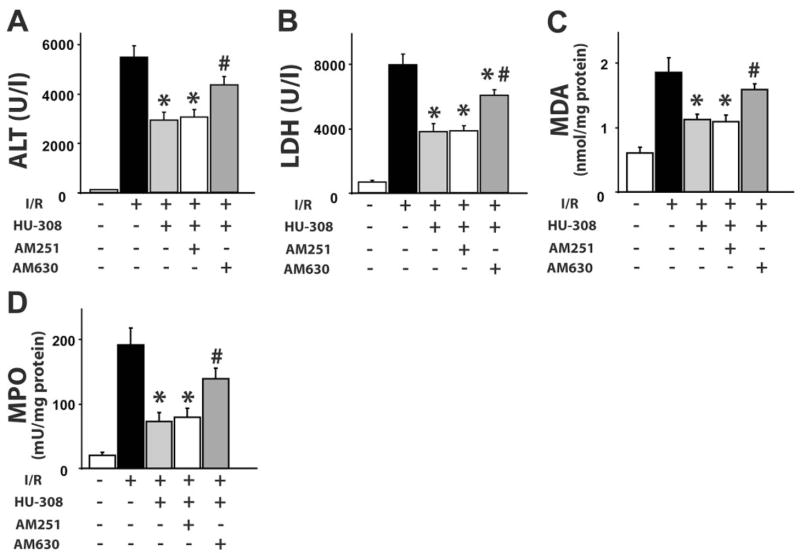
For assessment of tissue damage of the postischemic liver, the serum transaminase ALT and LDH activities were measured. After 60 min of ischemia and a subsequent 120-min reperfusion (60/120 min I/R), there was a dramatic increase in serum ALT and LDH activities in vehicle-treated C57Bl6/J mice as compared with sham-operated controls (Fig. 1, A and B). Pretreatment with 10 mg/kg CB2 agonist HU-308 significantly reduced the transaminase and LDH level following I/R, and this effect was not prevented by the CB1-selective antagonist AM251 but was attenuated significantly by the CB2 antagonist AM630. HU-308 (10 mg/kg) also significantly attenuated the I/R-induced tissue damage when administered right before the 120-min reperfusion [ALT: 5338±631 vs. 3351±570 (n=6; P=0.042); LDH: 7575±832 vs. 4729±878 (n=6; P=0.040), respectively].
Fig. 1.
CB2 agonist limits liver I/R-induced damage, lipid peroxidation, and neutrophil infiltration. (A) Serum transaminase ALT and (B) LDH levels; (C) liver MDA level and (D) MPO activity in sham or in mice exposed to 60/120 min I/R, pretreated with vehicle, HU-308 (10 mg/kg), AM251 (1 mg/kg) + HU-308, or AM630 (1 mg/kg) + HU-308 (n=7–12/each group; *, P<0.05, vs. I/R; #, P<0.05, versus I/R+HU-308).
The rate of lipid peroxidation was low in sham-operated mice, as indicated by the low MDA content, which nearly doubled following 60/120 min I/R, and this increase was attenuated in mice pretreated with HU-308, an effect preventable by AM630 pretreatment (Fig. 1C).
An important factor in the tissue damage following I/R is the neutrophil infiltration, an indicator of which is tissue MPO activity. In sham-operated, wild-type mice, MPO activity was barely detectable (Fig. 1D). Sixty/120 min I/R induced a marked increase in MPO activity, which was attenuated by HU-308. AM630 pretreatment attenuated the effect of HU-308.
CB2 agonist attenuates I/R-induced proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression in liver and serum
Sixty/120 min I/R greatly increased the levels of TNF-α, MIP-1α, and MIP-2 in the serum and in liver homogenates, as detected by ELISA (Fig. 2, A and B). HU-308 attenuated the I/R-induced increase significantly in cytokine levels in liver and serum, whereas AM630 pretreatment attenuated these effects of HU-308 (Fig. 2, A and B).
Fig. 2.
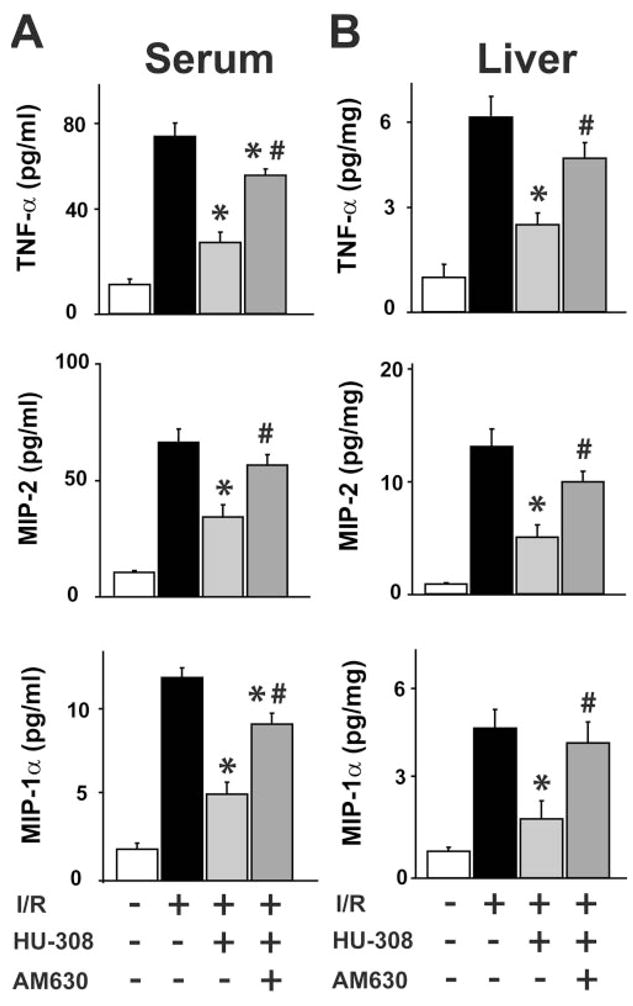
CB2 receptor agonist decreases proinflammatory markers in serum and liver. (A and B) TNF-α, MIP-2, and MIP-1α and levels in serum and liver tissue, measured by ELISA in sham or in mice exposed to 60/120 min I/R, pretreated with vehicle, HU-308 (10 mg/kg), or AM630 (1 mg/kg) + HU-308 (n=6–12/each group; *, P<0.05, vs. I/R; #, P<0.05, vs. I/R+HU-308).
CB2 agonist attenuates I/R-induced hepatic apoptosis
Sixty/120 min I/R increased caspase 3 activity and DNA fragmentation greatly (Fig. 3, A and B). HU-308 attenuated the I/R-induced, increased caspase 3 activity and DNA fragmentation significantly (Fig. 3, A and B).
Fig. 3.
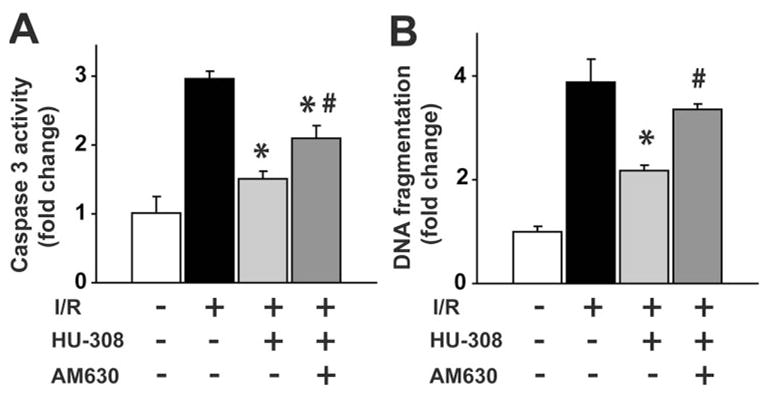
CB2 receptor agonist decreases I/R-induced apoptosis. (A) Caspase 3 activity and (B) DNA fragmentation in sham or in mice exposed to 60/120 min I/R, pretreated with vehicle, HU-308 (10 mg/kg), or AM630 (1 mg/kg) + HU-308 (n=6–8/each group; *, P<0.05, vs. I/R; #, P<0.05, vs. I/R+HU-308).
CB2 agonist improves I/R-induced hepatic histopathology
Sham-operated mice showed normal hepatic histology (Fig. 4A). In mice, 24 h following ischemic injury (60 min I), there was a marked degree of reperfusion damage indicated by the necrosis of hepatocytes in the pericentral and midzonal regions and by the massive neutrophil infiltration in the damaged areas (Fig. 4, A and B). The tissue injury and neutrophil infiltration were less pronounced in the HU-308-treated group (Fig. 4, A and B).
Fig. 4.
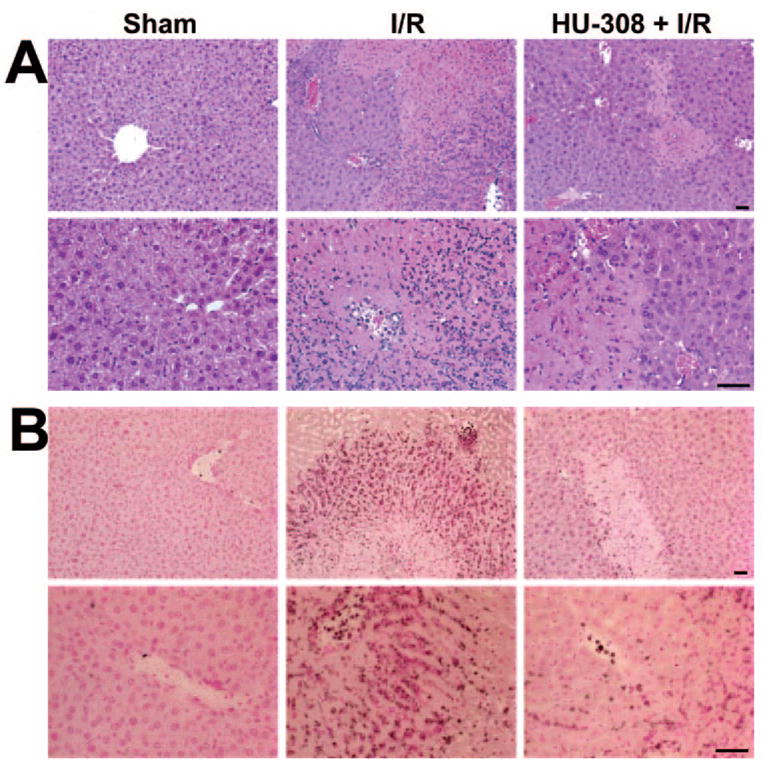
CB2 receptor agonist decreases histological damage and neutrophil infiltration 24 h following ischemia. Representative liver sections of sham mice, of mice exposed to 1 h/24 h I/R with vehicle, or HU-308 pretreatment. (A) H&E staining. (B) MPO staining (brown) contrastained with nuclear fast red. A similar histological profile was seen in three to four livers/group. The original scale bars indicate 50 μm.
CB2 agonist mitigates TNF-α-induced ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression in HLSECs
HLSECs have CB2 receptors measured by RT-PCR (Fig. 5A). TNF-α (50 ng/ml) treatment of HLSECs for 4 h resulted in robust activation of ICAM-1 (approximately fivefold, Fig. 5, B and C) and VCAM-1 (approximately fourfold, Fig. 5, D and E), respectively, when compared with control. HU-308 (0.5–4 μM) dose-dependently inhibited the TNF-α-induced, increased expression levels of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 (Fig. 5, B and D), which was attenuated by a CB2 antagonist (AM630; 1 μM) but not CB1 antagonists (AM251; 1 3M; Fig. 5, C and E). Antagonists had no effect in controls or TNF-α-treated cells.
Fig. 5.
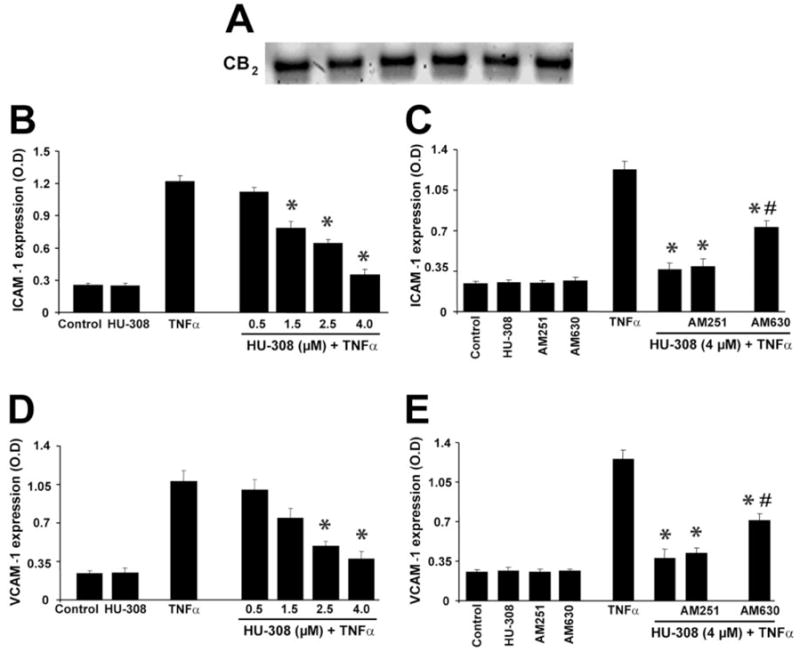
CB2 receptor agonist decreases TNF-α-induced overexpression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in HLSECs. (A) CB2 receptor expression in HLSECs (RT-PCR). (B and C) ICAM-1 expression; (D and E) VCAM-1 expression (*, P<0.05, vs. TNF-α; #, P<0.05, vs. TNF-α+HU-308; n=9).
CB2 agonist inhibits TNF-α-induced PMN adhesion to HLSECs
TNF-α (50 ng/ml) treatment resulted in enhanced PMN adhesion to HLSECs (~3.5-fold) compared with control (Fig. 6). HU-308 (4 μM) pretreatment markedly inhibited TNF-α-induced PMN adhesion to HLSECs, and this effect was attenuated by CB2 antagonists, which had no effect in controls or TNF-α-treated cells on PMN adhesion.
Fig. 6.
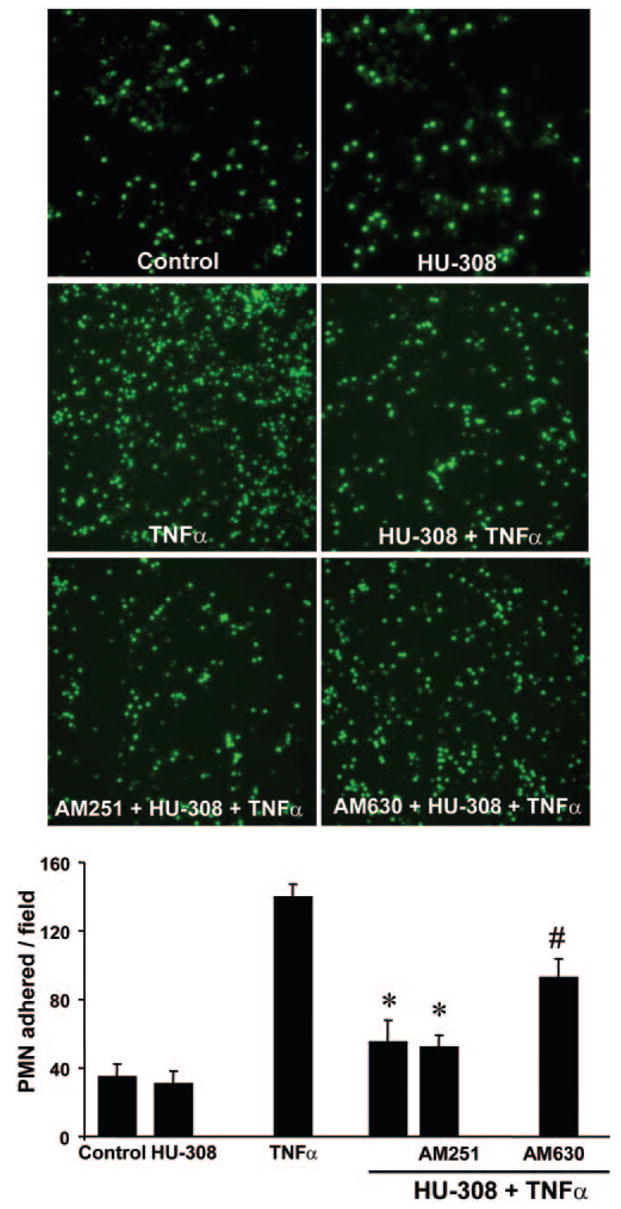
CB2 antagonist attenuates TNF-α-induced neutrophil adhesion to HLSECs. Representative images and quantification of human neutrophil adhesion to human liver endothelial cells. (*, P<0.05, vs. TNF-α; #, P<0.05, vs. TNF-α + HU-308; n=4).
DISCUSSION
There is considerable interest in the development of selective CB2 receptor agonists, which are devoid of psychoactive properties of CB1 agonists, for various inflammatory disorders. Earlier studies hypothesized that endocannabinoids or canna-binergic ligands, acting via a CB1/CB2-dependent or CB1/CB2-independent mechanism, may exert protective effects in various forms of preconditioning (including ischemic) of the myocardium (reviewed in refs. [14, 39, 41]). However, these studies used buffer-perfused, isolated heart preparations and could not address the question of whether endocannabinoids or synthetic agonists can modulate endothelial or immune cell activation and interactions, which are pivotal events in the sequel of reperfusion damage [14, 39]. In a more relevant study by using nonselective CB agonist WIN55212-2 and CB2 antagonist AM630 in a mouse model of myocardial I/R, the reduction of leukocyte-dependent myocardial damage could be attributed to CB2 receptor activation, as the protection afforded by WIN55212-2 could be prevented by AM630 but not by CB1 antagonist AM251 [46]. In agreement with those findings, we have recently reported that CB2 agonist JWH133 afforded protection against hepatic I/R damage by decreasing inflammatory cell infiltration and consequent tissue injury, and CB2 receptor knockout mice developed increased injury and proinflammatory phenotype following I/R [44].
In the present study, by using a more selective CB2 receptor agonist HU-308 [43], we aimed to delineate the role of CB2 receptor activation in an in vivo model of hepatic I/R and in TNF-α-induced ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression in HLSECs and adhesion of human neutrophils to HLSECs in vitro. In addition, we have studied the effect of CB2 stimulation on I/R-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis. We found that pretreatment of mice with HU-308 decreases the I/R-induced tissue damage, inflammatory cell infiltration, tissue and serum TNF-α, MIP-1α, and MIP-2 levels, tissue lipid peroxidation, and apoptosis. It is important that the beneficial effect of HU-308 was also preserved when injected right before reocclusion. CB2 receptor was expressed in HLSECs, and its activation attenuated the TNF-α-induced ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression and adhesion of human neutrophils to HLSECs in vitro. These results are in agreement with a recent study demonstrating that selective CB2 agonists (O-3853, O-1966) significantly decrease cerebral infarction and improve motor function after 1 h middle cerebral artery occlusion, followed by 23 h reperfusion in mice, presumable by attenuating the transient-ischemia-induced increase in leukocyte rolling and adhesion to vascular endothelial cells [47]. The role of CB2 receptors in I/R injury is supported further by increased accumulation of CB2-positive macrophages derived from resident microglia and/or invading monocytes following cerebral I/R [48]. Several studies have reported increased endocannabinoid levels following cerebral [18, 49–52] and hepatic I/R injury [44, 53]; however, the role of endocannabinoids in I/R injury remains to be a controversial issue requiring further clarification. One possibility is that endocannabinoids released during I/R may try to limit the hepatic injury by modulating the expression of adhesion molecules and the infiltration and activation of inflammatory cells (mononuclear and polymorpho-nuclear leukocytes are known to express CB2 receptors [6, 21]) by CB2-dependent mechanisms.
Adhesion molecules mediate the initial attachment of neutrophils to the activated endothelium [54, 55], which is a crucial event in initiation of liver I/R injury [55–58]. On reperfusion, TNF-α acts as a continuous stimulator for neutrophil infiltration in the liver, and it also up-regulates the production of chemokines, which may contribute to the up-regulation of cell adhesion molecules and neutrophil activation as well [57]. The increased inflammatory response aggravates oxidative stress further and initiates a vicious cycle, eventually culminating in cell death and organ dysfunction.
In conclusion, our results suggest that CB2 agonists may protect against hepatic and perhaps other organ I/R injuries by decreasing the endothelial cell activation, the expression of adhesion molecules ICAM-1 and VCAM-1, TNF-α, chemokine (MIP-1α and MIP-2) levels, neutrophil infiltration, lipid peroxidation, and apoptosis. Further studies should also establish the therapeutic window of protection during the reperfusion phase with CB2 receptor agonists to devise clinically relevant treatment strategies against various forms of I/R. Nevertheless, the beneficial effect of HU-308 observed in our model of I/R coupled with the absence of psychoactive effects of CB2 stimulation and the recently observed antifibrotic effects of CB2 receptor in the liver [59] suggest that this approach may represent a novel, promising strategy against hepatic and possibly other forms of I/R injury. Although HU-308 is one of the most selective CB2 agonists available, as with all drugs, it cannot be excluded entirely that it might have additional beneficial properties not related to CB2 receptor stimulation.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Intramural Research Program of NIH/NIAAA (to P. P.).
References
- 1.Fan C, Zwacka RM, Engelhardt JF. Therapeutic approaches for ischemia/reperfusion injury in the liver. J Mol Med. 1999;77:577–592. doi: 10.1007/s001099900029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jaeschke H, Lemasters JJ. Apoptosis versus oncotic necrosis in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1246–1257. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(03)01209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kupiec-Weglinski JW, Busuttil RW. Ischemia and reperfusion injury in liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2005;37:1653–1656. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2005.03.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Husted TL, Lentsch AB. Anti-inflammatory approaches to the prevention of ischemia/reperfusion injury in solid organ transplantation. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2005;6:508–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Szabo G, Bahrle S. Role of nitrosative stress and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activation in myocardial reperfusion injury. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2005;3:215–220. doi: 10.2174/1570161054368599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pacher P, Nivorozhkin A, Szabo C. Therapeutic effects of xanthine oxidase inhibitors: renaissance half a century after the discovery of allopurinol. Pharmacol Rev. 2006;58:87–114. doi: 10.1124/pr.58.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pacher P, Beckman JS, Liaudet L. Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:315–424. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00029.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Di Marzo V, Bifulco M, De Petrocellis L. The endocannabinoid system and its therapeutic exploitation. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:771–784. doi: 10.1038/nrd1495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Massa F, Storr M, Lutz B. The endocannabinoid system in the physiology and pathophysiology of the gastrointestinal tract. J Mol Med. 2005;83:944–954. doi: 10.1007/s00109-005-0698-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gabbay E, Avraham Y, Ilan Y, Israeli E, Berry EM. Endocannabinoids and liver disease—review. Liver Int. 2005;25:921–926. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2005.01180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zamora-Valdes D, Ponciano-Rodriguez G, Chavez-Tapia NC, Mendez-Sanchez N. The endocannabinoid system in chronic liver disease. Ann Hepatol. 2005;4:248–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pacher P, Batkai S, Kunos G. Cirrhotic cardiomyopathy: an endocannabinoid connection? Br J Pharmacol. 2005;146:313–314. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mallat A, Lotersztajn S. Endocannabinoids as novel mediators of liver diseases. J Endocrinol Invest. 2006;29:58–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pacher P, Batkai S, Kunos G. The endocannabinoid system as an emerging target of pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol Rev. 2006;58:389–462. doi: 10.1124/pr.58.3.2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kunos G, Osei-Hyiaman D, Batkai S, Gao B. Cannabinoids hurt, heal in cirrhosis. Nat Med. 2006;12:608–610. doi: 10.1038/nm0606-608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Panikashvili D, Shein NA, Mechoulam R, Trembovler V, Kohen R, Alexandrovich A, Shohami E. The endocannabinoid 2-AG protects the blood-brain barrier after closed head injury and inhibits mRNA expression of proinflammatory cytokines. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;22:257–264. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2005.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Panikashvili D, Mechoulam R, Beni SM, Alexandrovich A, Shohami E. CB1 cannabinoid receptors are involved in neuroprotection via NF-κ B inhibition. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005;25:477–484. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Panikashvili D, Simeonidou C, Ben-Shabat S, Hanus L, Breuer A, Mechoulam R, Shohami E. An endogenous cannabinoid (2-AG) is neuroprotective after brain injury. Nature. 2001;413:527–531. doi: 10.1038/35097089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mechoulam R, Spatz M, Shohami E. Endocannabinoids and neuroprotection. Sci STKE 2002. 2002:RE5. doi: 10.1126/stke.2002.129.re5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mechoulam R, Panikashvili D, Shohami E. Cannabinoids and brain injury: therapeutic implications. Trends Mol Med. 2002;8:58–61. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4914(02)02276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Klein TW. Cannabinoid-based drugs as anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:400–411. doi: 10.1038/nri1602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Matsuda LA, Lolait SJ, Brownstein MJ, Young AC, Bonner TI. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature. 1990;346:561–564. doi: 10.1038/346561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Batkai S, Pacher P, Osei-Hyiaman D, Radaeva S, Liu J, Harvey-White J, Offertaler L, Mackie K, Rudd MA, Bukoski RD, Kunos G. Endocannabinoids acting at cannabinoid-1 receptors regulate cardiovascular function in hypertension. Circulation. 2004;110:1996–2002. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000143230.23252.D2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pacher P, Batkai S, Osei-Hyiaman D, Offertaler L, Liu J, Harvey-White J, Brassai A, Jarai Z, Cravatt BF, Kunos G. Hemo-dynamic profile, responsiveness to anandamide, and baroreflex sensitivity of mice lacking fatty acid amide hydrolase. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;289:H533–H541. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00107.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gebremedhin D, Lange AR, Campbell WB, Hillard CJ, Harder DR. Cannabinoid CB1 receptor of cat cerebral arterial muscle functions to inhibit L-type Ca2+ channel current. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:H2085–H2093. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1999.276.6.H2085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Liu J, Gao B, Mirshahi F, Sanyal AJ, Khanolkar AD, Makriyannis A, Kunos G. Functional CB1 cannabinoid receptors in human vascular endothelial cells. Biochem J. 2000;346:835–840. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Batkai S, Jarai Z, Wagner JA, Goparaju SK, Varga K, Liu J, Wang L, Mirshahi F, Khanolkar AD, Makriyannis A, Urbaschek R, Garcia N, Jr, Sanyal AJ, Kunos G. Endocannabinoids acting at vascular CB1 receptors mediate the vasodilated state in advanced liver cirrhosis. Nat Med. 2001;7:827–832. doi: 10.1038/89953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Engeli S, Bohnke J, Feldpausch M, Gorzelniak K, Janke J, Batkai S, Pacher P, Harvey-White J, Luft FC, Sharma AM, Jordan J. Activation of the peripheral endocannabinoid system in human obesity. Diabetes. 2005;54:2838–2843. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.10.2838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Osei-Hyiaman D, DePetrillo M, Pacher P, Liu J, Radaeva S, Batkai S, Harvey-White J, Mackie K, Offertaler L, Wang L, Kunos G. Endocannabinoid activation at hepatic CB1 receptors stimulates fatty acid synthesis and contributes to diet-induced obesity. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:1298–1305. doi: 10.1172/JCI23057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Teixeira-Clerc F, Julien B, Grenard P, Tran Van Nhieu J, Deveaux V, Li L, Serriere-Lanneau V, Ledent C, Mallat A, Lotersztajn S. CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonism: a new strategy for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Nat Med. 2006;12:671–676. doi: 10.1038/nm1421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Munro S, Thomas KL, Abu-Shaar M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature. 1993;365:61–65. doi: 10.1038/365061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Van Sickle MD, Duncan M, Kingsley PJ, Mouihate A, Urbani P, Mackie K, Stella N, Makriyannis A, Piomelli D, Davison JS, Marnett LJ, Di Marzo V, Pittman QJ, Patel KD, Sharkey KA. Identification and functional characterization of brainstem cannabinoid CB2 receptors. Science. 2005;310:329–332. doi: 10.1126/science.1115740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mukhopadhyay P, Batkai S, Rajesh M, Czifra N, Harvey-White J, Hasko G, Zsengeller Z, Gerard NP, Liaudet L, Kunos G, Pacher P. Pharmacological inhibition of cannabinoid receptor-1 protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50:528–536. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.03.057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Shmist YA, Goncharov I, Eichler M, Shneyvays V, Isaac A, Vogel Z, Shainberg A. δ-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol protects cardiac cells from hypoxia via CB2 receptor activation and nitric oxide production. Mol Cell Biochem. 2006;283:75–83. doi: 10.1007/s11010-006-2346-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zoratti C, Kipmen-Korgun D, Osibow K, Malli R, Graier WF. Anandamide initiates Ca(2+) signaling via CB2 receptor linked to phospholipase C in calf pulmonary endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2003;140:1351–1362. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Golech SA, McCarron RM, Chen Y, Bembry J, Lenz F, Mechoulam R, Shohami E, Spatz M. Human brain endothelium: coexpression and function of vanilloid and endocannabinoid receptors. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004;132:87–92. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.08.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Blazquez C, Casanova ML, Planas A, Del Pulgar TG, Villanueva C, Fernandez-Acenero MJ, Aragones J, Huffman JW, Jorcano JL, Guzman M. Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by cannabinoids. FASEB J. 2003;17:529–531. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0795fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mestre L, Correa F, Docagne F, Clemente D, Guaza C. The synthetic cannabinoid WIN 55,212-2 increases COX-2 expression and PGE2 release in murine brain-derived endothelial cells following Theiler’s virus infection. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;72:869–880. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.06.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Pacher P, Batkai S, Kunos G. Cardiovascular pharmacology of cannabinoids. Handb Exp Pharmacol 2005. 2005:599–625. doi: 10.1007/3-540-26573-2_20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Pacher P, Batkai S, Kunos G. Blood pressure regulation by endocannabinoids and their receptors. Neuropharmacology. 2005;48:1130–1138. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2004.12.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lamontagne D, Lepicier P, Lagneux C, Bouchard JF. The endogenous cardiac cannabinoid system: a new protective mechanism against myocardial ischemia. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2006;99:242–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Pertwee RG. Pharmacological actions of cannabinoids. Handb Exp Pharmacol 2005. 2005:1–51. doi: 10.1007/3-540-26573-2_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hanus L, Breuer A, Tchilibon S, Shiloah S, Goldenberg D, Horowitz M, Pertwee RG, Ross RA, Mechoulam R, Fride E. HU-308: a specific agonist for CB(2), a peripheral cannabinoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:14228–14233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.25.14228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Batkai S, Osei-Hyiaman D, Pan H, El-Assal O, Rajesh M, Mukhopadhyay P, Hong F, Harvey-White J, Jafri A, Hasko G, Huffman JW, Gao B, Kunos G, Pacher P. Cannabinoid-2 receptor mediates protection against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. FASEB J. 2007;21:1788–1800. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-7451com. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Liaudet L, Murthy KG, Mabley JG, Pacher P, Soriano FG, Salzman AL, Szabo C. Comparison of inflammation, organ damage, and oxidant stress induced by Salmonella enterica serovar Muenchen flagellin and serovar Enteritidis lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 2002;70:192–198. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.1.192-198.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Di Filippo C, Rossi F, Rossi S, D’Amico M. Cannabinoid CB2 receptor activation reduces mouse myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: involvement of cytokine/chemokines and PMN. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;75:453–459. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0703303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zhang M, Martin BR, Adler MW, Razdan RK, Jallo JI, Tuma RF. Cannabinoid CB(2) receptor activation decreases cerebral infarction in a mouse focal ischemia/reperfusion model. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27:1387–1396. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ashton JC, Rahman RM, Nair SM, Sutherland BA, Glass M, Appleton I. Cerebral hypoxia-ischemia and middle cerebral artery occlusion induce expression of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor in the brain. Neurosci Lett. 2007;412:114–117. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.10.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Schmid PC, Krebsbach RJ, Perry SR, Dettmer TM, Maasson JL, Schmid HH. Occurrence and postmortem generation of anandamide and other long-chain N-acylethanolamines in mammalian brain. FEBS Lett. 1995;375:117–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01194-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Schabitz WR, Giuffrida A, Berger C, Aschoff A, Schwaninger M, Schwab S, Piomelli D. Release of fatty acid amides in a patient with hemispheric stroke: a microdialysis study. Stroke. 2002;33:2112–2114. doi: 10.1161/01.str.0000023491.63693.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Berger C, Schmid PC, Schabitz WR, Wolf M, Schwab S, Schmid HH. Massive accumulation of N-acylethanolamines after stroke. Cell signaling in acute cerebral ischemia? J Neurochem. 2004;88:1159–1167. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Muthian S, Rademacher DJ, Roelke CT, Gross GJ, Hillard CJ. Anandamide content is increased and CB1 cannabinoid receptor blockade is protective during transient, focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience. 2004;129:743–750. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.08.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kurabayashi M, Takeyoshi I, Yoshinari D, Matsumoto K, Maruyama I, Morishita Y. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol increases in ischemia-reperfusion injury of the rat liver. J Invest Surg. 2005;18:25–31. doi: 10.1080/08941930590905189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Carlos TM, Harlan JM. Leukocyte-endothelial adhesion molecules. Blood. 1994;84:2068–2101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Jaeschke H. Cellular adhesion molecules: regulation and functional significance in the pathogenesis of liver diseases. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:G602–G611. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1997.273.3.G602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Jaeschke H, Smith CW, Clemens MG, Ganey PE, Roth RA. Mechanisms of inflammatory liver injury: adhesion molecules and cytotoxicity of neutrophils. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1996;139:213–226. doi: 10.1006/taap.1996.0160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Jaeschke H. Mechanisms of liver injury. II Mechanisms of neutrophil-induced liver cell injury during hepatic ischemia-reperfusion and other acute inflammatory conditions. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;290:G1083–G1088. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00568.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ohkohchi N, Shibuya H, Tsukamoto S, Sakurada M, Oikawa K, Terashima T, Satomi S. Kupffer’s cells modulate neutrophile activity by superoxide anion and tumor necrosis factor-δ in reperfusion injury of liver transplantation-mechanisms of radical generation and reperfusion injury after cold ischemia. Transplant Proc. 1999;31:1055–1058. doi: 10.1016/s0041-1345(98)01902-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Julien B, Grenard P, Teixeira-Clerc F, Van Nhieu JT, Li L, Karsak M, Zimmer A, Mallat A, Lotersztajn S. Antifibrogenic role of the cannabinoid receptor CB2 in the liver. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:742–755. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.12.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]