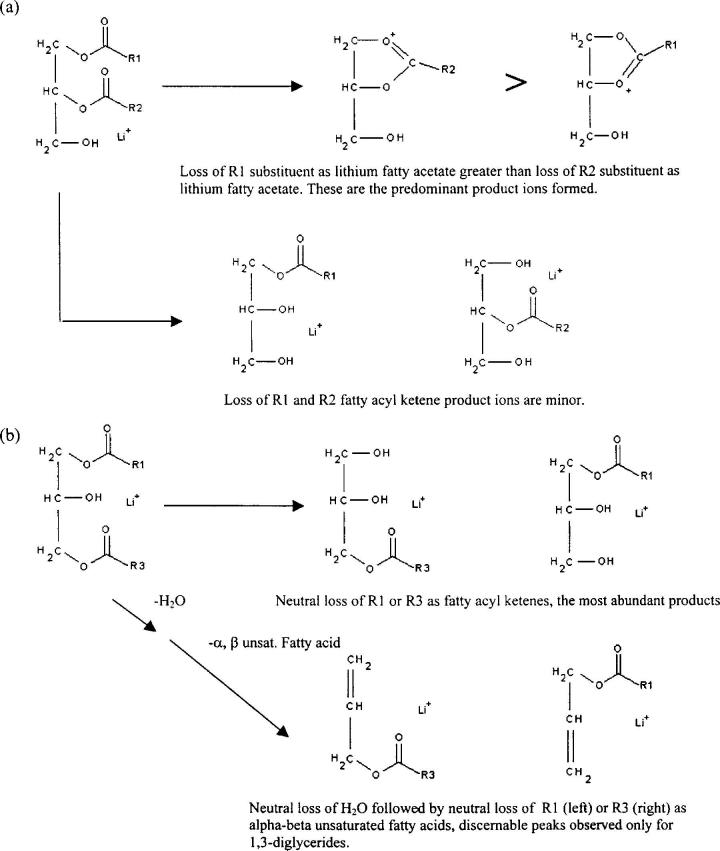
Figure 7.
General scheme for distinguishing asymmetric 1,2-diglycerides, and 1,2-diglycerides from 1,3-diglycerides based on MS/MS decompositions of lithium adducts. (a) Illustration of the use of product ion abundances for determining substituent location within an asymmetric 1,2-diglyceride. Loss of R1 substituent as lithium fatty acetate is greater than the R2 loss. Indicative of 1,2-diglycerides is that neutral losses of lithium fatty acetates are the predominant product ions. Bottom half of (a) shows that losses of fatty acyl ketenes yield minor product ions. Top half of (b) illustrates that the neutral losses of the R1 or the R3 substituent as fatty acyl ketenes are observed for the 1,3-diglyceride isomer, and these are the major product ions. Bottom part of (b) illustrates that the 1,3-diglyceride has a fragmentation pathway which results in the neutral loss of H2Owith subsequent loss of an α,β-unsaturated fatty acid. This fragmentation pathway is not observed for the 1,2-diglycerides.